Identification of VEGFs-related gene signature for predicting microangiogenesis and hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis
- PMID: 38874512
- PMCID: PMC11236318
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205931
Identification of VEGFs-related gene signature for predicting microangiogenesis and hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis
Abstract
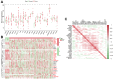
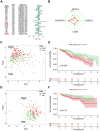
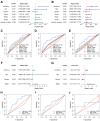
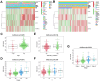
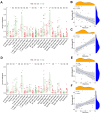
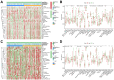
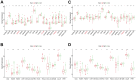
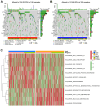
Microangiogenesis is an important prognostic factor in various cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) has been shown to contribute to tumor angiogenesis. Recently, several studies have investigated the regulation of VEGF production by a single gene, with few researchers exploring all genes that affect VEGF production. In this study, we comprehensively analyzed all genes affecting VEGF production in HCC and developed a risk model and gene-based risk score based on VEGF production. Moreover, the model's predictive capacity on prognosis of HCCs was verified using training and validation datasets. The developed model showed good prediction of the overall survival rate. Patients with a higher risk score experienced poor outcomes compared to those with a lower risk score. Furthermore, we identified the immunological causes of the poor prognosis of patients with high-risk scores comparing with those with low-risk scores.
Keywords: VEGF; gene signature; hepatocellular carcinoma; immune cell; microangiogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endoplasmic reticulum resident oxidase ERO1-Lalpha promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis and angiogenesis through the S1PR1/STAT3/VEGF-A pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Oct 30;9(11):1105. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1134-4. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30377291 Free PMC article.
-
A gene-based risk score model for predicting recurrence-free survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2021 Jan 5;21(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07692-6. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33402113 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of redox-immune based prognostic signature for hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Mar 10;18(9):2030-2041. doi: 10.7150/ijms.56289. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33850474 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and Validation of a Prognostic Gene-Based Model for Overall Survival Prediction in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using an Integrated Statistical and Bioinformatic Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 5;22(4):1632. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041632. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33562824 Free PMC article.
-
Antiangiogenic therapies for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncologist. 2013;18(4):430-8. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0388. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Oncologist. 2013. PMID: 23576483 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multipool-CEST and CEST-based pH assessment as predictive tools for glioma grading, IDH mutation, 1p/19q codeletion, and MGMT promoter methylation in gliomas.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 20;14:1507335. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1507335. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39759149 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akinyemiju T, Abera S, Ahmed M, Alam N, Alemayohu MA, Allen C, Al-Raddadi R, Alvis-Guzman N, Amoako Y, Artaman A, Ayele TA, Barac A, Bensenor I, et al. , and Global Burden of Disease Liver Cancer Collaboration. The Burden of Primary Liver Cancer and Underlying Etiologies From 1990 to 2015 at the Global, Regional, and National Level: Results From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. JAMA Oncol. 2017; 3:1683–91. 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3055 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

