Analysis of Top 100 Articles Cited in Top Pain Journals: A Comprehensive Two Decade Bibliometric Analysis
- PMID: 38874850
- PMCID: PMC11438724
- DOI: 10.1007/s11916-024-01273-z
Analysis of Top 100 Articles Cited in Top Pain Journals: A Comprehensive Two Decade Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
Purpose of review: A bibliometric analysis was performed to analyze and compare the top 100 articles from the most well-known five pain journals: Pain, Pain Physician, Pain Medicine, Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine, and Journal of Pain. A query of the Scopus database was performed to filter the top 200 most cited articles from each journal. CY score was calculated for the top 200 articles from each journal by dividing the total number of citations by the number of years the article has been published.
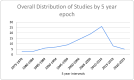
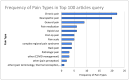
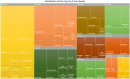
Recent findings: All articles had a collective analysis of the top CY scores, the top 100 of which were further analyzed. The pain subtype, type of publication, country of origin, and senior author were extrapolated from these top 100 articles. Frequency tables were organized, revealing Pain Journal as the highest publishing journal out of the top 100 articles. Chronic pain was the most studied subtype of pain and narrative reviews were the most common type of evidence. Studies were also organized in five-year epochs to analyze the frequency of publications in these intervals. Results show that 2010-2014 had the highest frequency of articles published overall. Journal Impact Factor (JIF) is also an objective indicator of the average number of citations per published article from each journal. The journal with the highest JIF was Pain with an impact factor of 7.926. (6).
Keywords: Journal of pain; Manuscript; Pain; Pain medicine; Pain physician journal; Regional anesthesia and pain medicine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Pain Physician. Updated February 2024. Accessed November 2023. https://www.painphysicianjournal.com/index.
-
- Pain: The Journal of the International Association for the Study of Pain. Accessed November 2023. https://journals.lww.com/pain/pages/default.aspx.
-
- Pain Medicine. Accessed November 2023. https://academic.oup.com/painmedicine.
-
- Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine. February 1, 2024. Accessed November 2023. https://rapm.bmj.com/.
-
- The Journal of Pain. Accessed November 2023. https://www.jpain.org/.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

