Effects of 3 days of citrulline malate supplementation on short-duration repeated sprint running performance in male team sport athletes
- PMID: 38874989
- PMCID: PMC11235799
- DOI: 10.1002/ejsc.12090
Effects of 3 days of citrulline malate supplementation on short-duration repeated sprint running performance in male team sport athletes
Abstract
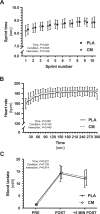
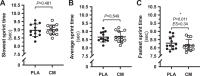
Citrulline malate (CM) is purported to be an ergogenic aid during various types of exercise performance. However, the effects of CM on repeated sprint performance (RSP) are under-explored. In a placebo-controlled, double-blind, counterbalanced cross-over design, male university-level team sport athletes (n = 13) performed two familiarization trials, after which CM or placebo (PLA) (8 × 1 g tablets each day) were taken on the 2 days prior to, and with breakfast on the morning of, each main experimental trial. The main experimental trials employed a RSP protocol consisting of 10 repetitions of 40 m maximal shuttle run test (MST) with a 30 s interval between the start of each sprint. Sprint times and heart rate were recorded throughout the MST, and blood lactate concentrations were measured before, immediately after, and 5 min after completing the MST. CM resulted in better RSP compared to PLA, as indicated by a lower sprint performance decrement (Sdec: CM, 4.68% ± 1.82% vs. PLA, 6.10% ± 1.83%; p = 0.03; ES = 0.77), which was possibly influenced by the fastest sprint time being faster in CM (CM, 8.16 ± 0.34 s vs. PLA, 8.29 ± 0.39 s; p = 0.011; ES = 0.34). There were no differences between CM and PLA in average sprint time (p = 0.54), slowest sprint time (p = 0.48), blood lactate concentrations (p = 0.73) or heart rate (p = 0.18), nor was there a condition × time interaction effect across the 10 sprints (p = 0.166). Three days of CM supplementation (8 g daily) attenuated the sprint performance decrement during short-duration high-intensity exercise in the form of running RSP in male university-level team sport athletes.
Keywords: ergogenic aid; lactate; maximal shuttle run test; performance decrement.
© 2024 The Authors. European Journal of Sport Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH on behalf of European College of Sport Science.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest, financial or otherwise, is declared by the authors.
Figures


References
-
- Bezuglov, E. , Morgans R., Lazarev A., Kalinin E., Butovsky M., Savin E., Tzgoev E., et al. 2022. “The Effect of a Single Dose of Citrulline on the Physical Performance of Soccer‐specific Exercise in Adult Elite Soccer Players (A Pilot Randomized Double‐Blind Trial).” Nutrients 14(23): 5036. 10.3390/nu14235036 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

