Global research landscape and emerging trends in Graves' disease: A bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 38875401
- PMCID: PMC11175884
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037963
Global research landscape and emerging trends in Graves' disease: A bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Background: Graves' disease is a prevalent thyroid disorder and is the primary cause of hyperthyroidism. Significant progress has been made in understanding the epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of this disease. However, bibliometric analyses on Graves' disease are lacking. We aimed to comprehensively summarize the research, progression, and focal points of Graves' disease through data mining and integrated analysis of the existing literature.
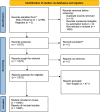
Methods: We retrieved relevant literature on Graves' disease from 2003 to 2023 from the Web of Science database. We performed bibliometric analysis using CiteSpace and the R package Bibliometrix.
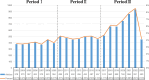
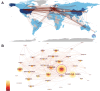
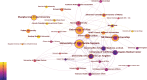
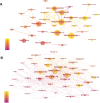
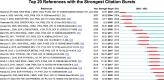
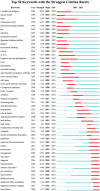
Results: We identified 10,901 publications from 132 countries, with a steady rise in the number of publications over the past 5 years. The US leads in publication volume, with the University of California System being the primary contributing institution. The journal Thyroid had the highest publication output, while the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism was the most frequently cited. These publications involved 2305 authors, with Antonelli Alessandro and Smith Terry being the most prolific. The most frequently cited articles were the "2016 American Thyroid Association guidelines for diagnosis and management of hyperthyroidism and other causes of thyrotoxicosis" and the "Thyroid Association/European Group on Graves' orbitopathy guidelines for the management of Graves' orbitopathy." Analysis of the bursts of cited references, keywords, and their clustering revealed that research on Graves' disease predominantly centers on clinical management, thyroid-stimulating hormone receptors, thyroid hormones, autoimmunity and inflammation, Graves' ophthalmopathy, thyroid nodules, and thyroid cancer.
Conclusion: This is the first comprehensive bibliometric study to summarize progress and trends in Graves' disease research. These results highlight recent research hotspots and promising directions, thereby providing a valuable reference for other scholars.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Trends in Graves' orbitopathy research in the past two decades: a bibliometric analysis.Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2022 Feb 14;85(6):590-598. doi: 10.5935/0004-2749.20220081. eCollection 2022. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2022. PMID: 35170638 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Insights in Thyroid Eye Disease Research from 2010 to 2022: Trends, Hot Spots, and Research Situation.Semin Ophthalmol. 2025 Apr 14:1-13. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2025.2490669. Online ahead of print. Semin Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40223741
-
Evolution and global research trends of immunity in diabetic nephropathy: a bibliometric and visual analysis from 2004 to 2023.Int Urol Nephrol. 2024 Oct;56(10):3307-3321. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04081-x. Epub 2024 May 17. Int Urol Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38758346 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging research themes in maternal hypothyroidism: a bibliometric exploration.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 26;15:1370707. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1370707. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38596686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global trends and hotspots of treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A bibliometric and visualization analysis (2010-2023).World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Oct 7;29(37):5339-5360. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i37.5339. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37899789 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wémeau JL, Klein M, Sadoul JL, Briet C, Vélayoudom-Céphise FL. Graves’ disease: introduction, epidemiology, endogenous and environmental pathogenic factors. Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2018;79:599–607. - PubMed
-
- Antonelli A, Fallahi P, Elia G, et al. . Graves’ disease: clinical manifestations, immune pathogenesis (cytokines and chemokines) and therapy. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;34:101388. - PubMed
-
- Antonelli A, Ferrari SM, Ragusa F, et al. . Graves’ disease: epidemiology, genetic and environmental risk factors and viruses. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;34:101387. - PubMed
-
- Vejrazkova D, Vcelak J, Vaclavikova E, et al. . Genetic predictors of the development and recurrence of Graves’ disease. Physiol Res. 2018;67(Suppl 3):S431–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

