Validation of a Novel Noninvasive Technology to Estimate Blood Oxygen Saturation Using Green Light: Observational Study
- PMID: 38875701
- PMCID: PMC11041477
- DOI: 10.2196/46974
Validation of a Novel Noninvasive Technology to Estimate Blood Oxygen Saturation Using Green Light: Observational Study
Abstract
Background: Pulse oximeters work within the red-infrared wavelengths. Therefore, these oximeters produce erratic results in dark-skinned subjects and in subjects with cold extremities. Pulse oximetry is routinely performed in patients with fever; however, an elevation in body temperature decreases the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen, causing a drop in oxygen saturation or oxyhemoglobin concentrations.
Objective: We aimed to determine whether our new investigational device, the Shani device or SH1 (US Patent 11191460), detects a drop in oxygen saturation or a decrease in oxyhemoglobin concentrations.
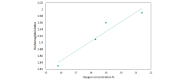
Methods: An observational study (phase 1) was performed in two separate groups to validate measurements of hemoglobin and oxygen concentrations, including 39 participants recruited among current university students and staff aged 20-40 years. All volunteers completed baseline readings using the SH1 device and the commercially available Food and Drug Administration-approved pulse oximeter Masimo. SH1 uses two light-emitting diodes in which the emitted wavelengths match with absorption peaks of oxyhemoglobin (hemoglobin combined with oxygen) and deoxyhemoglobin (hemoglobin without oxygen or reduced hemoglobin). Total hemoglobin was calculated as the sum of oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin. Subsequently, 16 subjects completed the "heat jacket study" and the others completed the "blood donation study." Masimo was consistently used on the finger for comparison. The melanin level was accounted for using the von Luschan skin color scale (VLS) and a specifically designed algorithm. We here focus on the results of the heat jacket study, in which the subject wore a double-layered heated jacket and pair of trousers including a network of polythene tubules along with an inlet and outlet. Warm water was circulated to increase the body temperature by 0.5-0.8 °C above the baseline body temperature. We expected a slight drop in oxyhemoglobin concentrations in the heating phase at the tissue level.
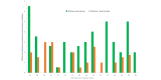
Results: The mean age of the participants was 24.1 (SD 0.8) years. The skin tone varied from 12 to 36 on the VLS, representing a uniform distribution with one-third of the participants having fair skin, brown skin, and dark skin, respectively. Using a specific algorithm and software, the reflection ratio for oxyhemoglobin was displayed on the screen of the device along with direct hemoglobin values. The SH1 device picked up more minor changes in oxyhemoglobin levels after a change in body temperature compared to the pulse oximeter, with a maximum drop in oxyhemoglobin concentration detected of 6.5% and 2.54%, respectively.
Conclusions: Our new investigational device SH1 measures oxygen saturation at the tissue level by reflectance spectroscopy using green wavelengths. This device fared well regardless of skin color. This device can thus eliminate racial disparity in these key biomarker assessments. Moreover, since the light is shone on the wrist, SH1 can be readily miniaturized into a wearable device.
Keywords: oxygen level; oxygen saturation; oxyhemoglobin concentration; pulse oximeter; racial disparity; reflectance spectroscopy; tissue oxygen measurements.
©Sanjay Gokhale, Vinoop Daggubati, Georgios Alexandrakis. Originally published in JMIR Biomedical Engineering (http://biomsedeng.jmir.org), 27.03.2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Lahav DZ, Picard E, Mimouni F, Joseph L, Goldberg S. The effect of fever on blood oxygen saturation in children. Harefuah. 2015 Mar;154(3):162–165, 213, 212. - PubMed
-
- Fawzy A, Wu TD, Wang K, Robinson ML, Farha J, Bradke A, Golden SH, Xu Y, Garibaldi BT. Racial and ethnic discrepancy in pulse oximetry and delayed identification of treatment eligibility among patients with COVID-19. JAMA Intern Med. 2022 Jul 01;182(7):730–738. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.1906. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/35639368 2792653 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zonios G, Bykowski J, Kollias N. Skin melanin, hemoglobin, and light scattering properties can be quantitatively assessed in vivo using diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. J Invest Dermatol. 2001 Dec;117(6):1452–1457. doi: 10.1046/j.0022-202x.2001.01577.x. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0022-202X(15)41483-6 S0022-202X(15)41483-6 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

