α-Ketoglutarate prevents hyperlipidemia-induced fatty liver mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress by activating the AMPK-pgc-1α/Nrf2 pathway
- PMID: 38875959
- PMCID: PMC11226981
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103230
α-Ketoglutarate prevents hyperlipidemia-induced fatty liver mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress by activating the AMPK-pgc-1α/Nrf2 pathway
Abstract
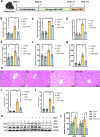
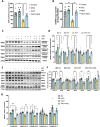
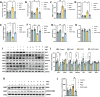
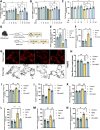
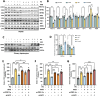
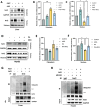
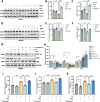
α-Ketoglutarate (AKG), a crucial intermediate in the tricarboxylic acid cycle, has been demonstrated to mitigate hyperlipidemia-induced dyslipidemia and endothelial damage. While hyperlipidemia stands as a major trigger for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, the protection of AKG on hyperlipidemia-induced hepatic metabolic disorders remains underexplored. This study aims to investigate the potential protective effects and mechanisms of AKG against hepatic lipid metabolic disorders caused by acute hyperlipidemia. Our observations indicate that AKG effectively alleviates hepatic lipid accumulation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and loss of redox homeostasis in P407-induced hyperlipidemia mice, as well as in palmitate-injured HepG2 cells and primary hepatocytes. Mechanistic insights reveal that the preventive effects are mediated by activating the AMPK-PGC-1α/Nrf2 pathway. In conclusion, our findings shed light on the role and mechanism of AKG in ameliorating abnormal lipid metabolic disorders in hyperlipidemia-induced fatty liver, suggesting that AKG, an endogenous mitochondrial nutrient, holds promising potential for addressing hyperlipidemia-induced fatty liver conditions.
Keywords: Fatty liver; Hyperlipidemia; Mitochondrial dysfunction; Nrf2; Oxidative stress; PGC-1α; α-Ketoglutarate (AKG).
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Moro E., Gallina P., Pais M., Cazzolato G., Alessandrini P., Bittolo-Bon G. Hypertriglyceridemia is associated with increased insulin resistance in subjects with normal glucose tolerance: evaluation in a large cohort of subjects assessed with the 1999 World Health Organization criteria for the classification of diabetes. Metabolism. 2003;52:616–619. doi: 10.1053/meta.2003.50102. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Korolenko T.A., Tuzikov F.V., Johnston T.P., Tuzikova N.A., Kisarova Y.A., Zhanaeva S.Y., Alexeenko T.V., Zhukova N.A., Brak I.V., Spiridonov V.K., et al. The influence of repeated administration of poloxamer 407 on serum lipoproteins and protease activity in mouse liver and heart. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2012;90:1456–1468. doi: 10.1139/y2012-118. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

