A designed ankyrin-repeat protein that targets Parkinson's disease-associated LRRK2
- PMID: 38876305
- PMCID: PMC11284679
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107469
A designed ankyrin-repeat protein that targets Parkinson's disease-associated LRRK2
Abstract
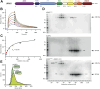
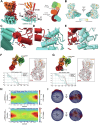
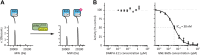
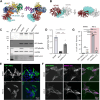
Leucine rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) is a large multidomain protein containing two catalytic domains, a kinase and a GTPase, as well as protein interactions domains, including a WD40 domain. The association of increased LRRK2 kinase activity with both the familial and sporadic forms of Parkinson's disease has led to an intense interest in determining its cellular function. However, small molecule probes that can bind to LRRK2 and report on or affect its cellular activity are needed. Here, we report the identification and characterization of the first high-affinity LRRK2-binding designed ankyrin-repeat protein (DARPin), named E11. Using cryo-EM, we show that DARPin E11 binds to the LRRK2 WD40 domain. LRRK2 bound to DARPin E11 showed improved behavior on cryo-EM grids, resulting in higher resolution LRRK2 structures. DARPin E11 did not affect the catalytic activity of a truncated form of LRRK2 in vitro but decreased the phosphorylation of Rab8A, a LRRK2 substrate, in cells. We also found that DARPin E11 disrupts the formation of microtubule-associated LRRK2 filaments in cells, which are known to require WD40-based dimerization. Thus, DARPin E11 is a new tool to explore the function and dysfunction of LRRK2 and guide the development of LRRK2 kinase inhibitors that target the WD40 domain instead of the kinase.
Keywords: DARPin; LRRK2; Parkinson’s disease; Rab8a; WD40; cryo-electron microscopy; kinase; kinase inhibitor; microtubule.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest SRP is a consultant for Schrodinger and Stoke Therapeutics. AP is a co-founder and shareholder of Molecular Partners who are commercializing the DARPin technology. All other authors do not have any conflicts to report with the contents of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of the WD40 domain dimer of LRRK2.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jan 29;116(5):1579-1584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1817889116. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30635421 Free PMC article.
-
LRRK2 Structure-Based Activation Mechanism and Pathogenesis.Biomolecules. 2023 Mar 28;13(4):612. doi: 10.3390/biom13040612. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37189360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The In Situ Structure of Parkinson's Disease-Linked LRRK2.Cell. 2020 Sep 17;182(6):1508-1518.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.004. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Cell. 2020. PMID: 32783917 Free PMC article.
-
Structural model of the dimeric Parkinson's protein LRRK2 reveals a compact architecture involving distant interdomain contacts.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Jul 26;113(30):E4357-66. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1523708113. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27357661 Free PMC article.
-
Roc, the G-domain of the Parkinson's disease-associated protein LRRK2.Trends Biochem Sci. 2022 Dec;47(12):1038-1047. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2022.06.009. Epub 2022 Jul 12. Trends Biochem Sci. 2022. PMID: 35840518 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Type II kinase inhibitors that target Parkinson's disease-associated LRRK2.Sci Adv. 2025 Jun 6;11(23):eadt2050. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adt2050. Epub 2025 Jun 4. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40465731 Free PMC article.
-
Type-II kinase inhibitors that target Parkinson's Disease-associated LRRK2.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 13:2024.09.17.613365. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.17.613365. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Sci Adv. 2025 Jun 6;11(23):eadt2050. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adt2050. PMID: 39554022 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Paisán-Ruíz C., Jain S., Evans E.W., Gilks W.P., Simón J., van der Brug M., et al. Cloning of the gene containing mutations that cause PARK8-linked Parkinson’s disease. Neuron. 2004;44:595–600. - PubMed
-
- Zimprich A., Biskup S., Leitner P., Lichtner P., Farrer M., Lincoln S., et al. Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron. 2004;44:601–607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

