Flexible parsing, interpretation, and editing of technical sequences with splitcode
- PMID: 38876979
- PMCID: PMC11193061
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae331
Flexible parsing, interpretation, and editing of technical sequences with splitcode
Abstract
Motivation: Next-generation sequencing libraries are constructed with numerous synthetic constructs such as sequencing adapters, barcodes, and unique molecular identifiers. Such sequences can be essential for interpreting results of sequencing assays, and when they contain information pertinent to an experiment, they must be processed and analyzed.
Results: We present a tool called splitcode, that enables flexible and efficient parsing, interpreting, and editing of sequencing reads. This versatile tool facilitates simple, reproducible preprocessing of reads from libraries constructed for a large array of single-cell and bulk sequencing assays.
Availability and implementation: The splitcode program is available at http://github.com/pachterlab/splitcode.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
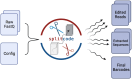
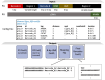
Update of
-
Flexible parsing, interpretation, and editing of technical sequences with splitcode.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 9:2023.03.20.533521. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.20.533521. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Bioinformatics. 2024 Jun 3;40(6):btae331. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae331. PMID: 36993532 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.

