Scanless two-photon voltage imaging
- PMID: 38876987
- PMCID: PMC11178882
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-49192-2
Scanless two-photon voltage imaging
Abstract
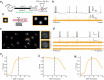
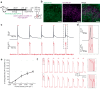
Two-photon voltage imaging has long been heralded as a transformative approach capable of answering many long-standing questions in modern neuroscience. However, exploiting its full potential requires the development of novel imaging approaches well suited to the photophysical properties of genetically encoded voltage indicators. We demonstrate that parallel excitation approaches developed for scanless two-photon photostimulation enable high-SNR two-photon voltage imaging. We use whole-cell patch-clamp electrophysiology to perform a thorough characterization of scanless two-photon voltage imaging using three parallel illumination approaches and lasers with different repetition rates and wavelengths. We demonstrate voltage recordings of high-frequency spike trains and sub-threshold depolarizations from neurons expressing the soma-targeted genetically encoded voltage indicator JEDI-2P-Kv. Using a low repetition-rate laser, we perform multi-cell recordings from up to fifteen targets simultaneously. We co-express JEDI-2P-Kv and the channelrhodopsin ChroME-ST and capitalize on their overlapping two-photon absorption spectra to simultaneously evoke and image action potentials using a single laser source. We also demonstrate in vivo scanless two-photon imaging of multiple cells simultaneously up to 250 µm deep in the barrel cortex of head-fixed, anaesthetised mice.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Update of
-
Scanless two-photon voltage imaging.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Jan 24:rs.3.rs-2412371. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2412371/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 14;15(1):5095. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49192-2. PMID: 36747617 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- ANR-17-CE16-0021/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- RF1 NS128901/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB032854/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- ANR-19-CE16-0026/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- ANR-10-LABX-65/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- RF1 NS133657/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD103555/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB027145/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- 442616457/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- U01 NS113294/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS118288/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS133971/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

