Ligand-based design of [18F]OXD-2314 for PET imaging in non-Alzheimer's disease tauopathies
- PMID: 38877019
- PMCID: PMC11178805
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-49258-1
Ligand-based design of [18F]OXD-2314 for PET imaging in non-Alzheimer's disease tauopathies
Abstract
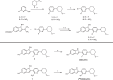
Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of tau aggregation in Alzheimer's disease (AD) is helping to map and quantify the in vivo progression of AD pathology. To date, no high-affinity tau-PET radiopharmaceutical has been optimized for imaging non-AD tauopathies. Here we show the properties of analogues of a first-in-class 4R-tau lead, [18F]OXD-2115, using ligand-based design. Over 150 analogues of OXD-2115 were synthesized and screened in post-mortem brain tissue for tau affinity against [3H]OXD-2115, and in silico models were used to predict brain uptake. [18F]OXD-2314 was identified as a selective, high-affinity non-AD tau PET radiotracer with favorable brain uptake, dosimetry, and radiometabolite profiles in rats and non-human primate and is being translated for first-in-human PET studies.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.S., D.S., and J.V. were employees of Oxiant Discovery during the conduct of the reported study who may own or hold stock options in the company. N.V. is a co-founder of MedChem Imaging, Inc., which did not contribute support for this study. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
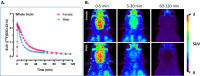
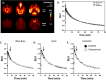
 ), cortex (triangles,
), cortex (triangles, ), and cerebellum (rings, (
), and cerebellum (rings, ( ) from baseline PET scan using [18F]OXD-2314 over 0–90 min. C–E Time-activity curves of SUV in macaque (n = 1) from a displacement PET experiment using [18F]OXD-2314 with unlabeled OXD-2314, (C) whole brain, (D) cortex, and (E) cerebellum. Baseline (
) from baseline PET scan using [18F]OXD-2314 over 0–90 min. C–E Time-activity curves of SUV in macaque (n = 1) from a displacement PET experiment using [18F]OXD-2314 with unlabeled OXD-2314, (C) whole brain, (D) cortex, and (E) cerebellum. Baseline ( ) and displacement ((
) and displacement (( ) PET imaging in macaque, 0–90 min. The displacing dose of unlabeled OXD-2314 (0.5 mg/kg) was administered at 10 min post-injection (indicated by arrows). No significant displacement of [18F]OXD-2314 could be detected in any brain region, as expected in animals without tau pathology.
) PET imaging in macaque, 0–90 min. The displacing dose of unlabeled OXD-2314 (0.5 mg/kg) was administered at 10 min post-injection (indicated by arrows). No significant displacement of [18F]OXD-2314 could be detected in any brain region, as expected in animals without tau pathology.
Similar articles
-
Radiosynthesis, In Vitro Characterization, and In Vivo PET Neuroimaging of [18F]F-4 for Tau Protein: A First-in-Human PET Study.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025 Mar 19;16(6):1182-1189. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.4c00866. Epub 2025 Mar 10. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40063537 Free PMC article.
-
Tau PET Imaging With [18F]MK-6240: Limited Affinity for Primary Tauopathies and High Specificity for Alzheimer's Disease.Eur J Neurol. 2025 Feb;32(2):e70068. doi: 10.1111/ene.70068. Eur J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39957301 Free PMC article.
-
Current Progress and Future Directions in Non-Alzheimer's Disease Tau PET Tracers.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025 Jan 15;16(2):111-127. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.4c00319. Epub 2025 Jan 6. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39762194 Review.
-
Discovery of 2-(4-(2-fluoroethoxy)piperidin-1-yl)-9-methyl-9H-pyrrolo[2,3-b:4,5-c']dipyridine ([18F]PI-2014) as PET tracer for the detection of pathological aggregated tau in Alzheimer's disease and other tauopathies.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Oct 15;204:112615. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112615. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32771872
-
Tau PET imaging in neurodegenerative tauopathies-still a challenge.Mol Psychiatry. 2019 Aug;24(8):1112-1134. doi: 10.1038/s41380-018-0342-8. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Mol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30635637 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Strategies of positron emission tomography (PET) tracer development for imaging of tau and α-synuclein in neurodegenerative disorders.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Nov 20. doi: 10.1039/d4md00576g. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39678127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Water-directed pinning is key to tau prion formation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 May 6;122(18):e2421391122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2421391122. Epub 2025 Apr 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40294272
-
Tau Imaging: Use and Implementation in New Diagnostic and Therapeutic Paradigms for Alzheimer's Disease.Geriatrics (Basel). 2025 Feb 14;10(1):27. doi: 10.3390/geriatrics10010027. Geriatrics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39997526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiosynthesis, In Vitro Characterization, and In Vivo PET Neuroimaging of [18F]F-4 for Tau Protein: A First-in-Human PET Study.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025 Mar 19;16(6):1182-1189. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.4c00866. Epub 2025 Mar 10. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40063537 Free PMC article.
-
First-in-human PET neuroimaging of [18F]OXD-2314.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025 Jun 24. doi: 10.1007/s00259-025-07413-w. Online ahead of print. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40553116
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

