C-reactive protein as robust laboratory value associated with prognosis in patients with stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with definitive radiochemotherapy
- PMID: 38877146
- PMCID: PMC11178931
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-64302-2
C-reactive protein as robust laboratory value associated with prognosis in patients with stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with definitive radiochemotherapy
Abstract
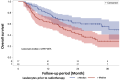
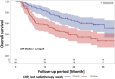
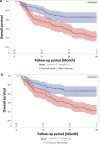
To evaluate the prognostic value of biomarkers from peripheral blood obtained as routine laboratory assessment for overall survival in a cohort of stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with definitive radiochemotherapy at a high-volume cancer center. Seven blood biomarkers from 160 patients treated with definitive radiochemotherapy for stage III NSCLC were analyzed throughout the course treatment. Parameters were preselected using univariable and multivariable proportional hazards analysis and were assessed for internal validity using leave-one-out cross validation. Cross validated classifiers including biomarkers in addition to important clinical parameters were compared with classifiers containing the clinical parameters alone. An increased C-reactive protein (CRP) value in the final week of radiotherapy was found as a prognostic factor for overall survival, both as a continuous (HR 1.099 (1.038-1.164), p < 0.0012) as well as categorical variable splitting data at the median value of 1.2 mg/dl (HR 2.214 (1.388-3.531), p < 0.0008). In the multivariable analysis, the CRP value-maintained significance with an HR of 1.105 (1.040-1.173) and p-value of 0.0012. The cross validated classifier using CRP at the end of radiotherapy in addition to clinical parameters separated equally sized high and low risk groups more distinctly than a classifier containing the clinical parameters alone (HR = 2.786 (95% CI 1.686-4.605) vs. HR = 2.287 (95% CI 1.407-3.718)). Thus, the CRP value at the end of radiation therapy has successfully passed the crucial cross-validation test. The presented data on CRP levels suggests that inflammatory markers may become increasingly important during definitive radiochemotherapy, particularly with the growing utilization of immunotherapy as a consolidation therapy for stage III NSCLC.
Keywords: C-reactive protein (CRP); Definitive radiochemotherapy; ESPATUE trial; Laboratory values; Overall survival; Stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pretreatment metabolic tumour volume in stage IIIA/B non-small-cell lung cancer uncovers differences in effectiveness of definitive radiochemotherapy schedules: analysis of the ESPATUE randomized phase 3 trial.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019 Jul;46(7):1439-1447. doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-4270-x. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30710323 Clinical Trial.
-
Heart dose exposure as prognostic marker after radiotherapy for resectable stage IIIA/B non-small-cell lung cancer: secondary analysis of a randomized trial.Ann Oncol. 2017 May 1;28(5):1084-1089. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx069. Ann Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28453703 Clinical Trial.
-
Elevated serum C-reactive protein, carcinoembryonic antigen and N2 disease are poor prognostic indicators in non-small cell lung cancer.Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2015 Dec;11(4):e22-30. doi: 10.1111/ajco.12091. Epub 2014 May 30. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 24889374
-
Definitive radiochemotherapy versus surgery within multimodality treatment in stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) - a cumulative meta-analysis of the randomized evidence.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 20;8(25):41670-41678. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16471. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28415831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune checkpoint-inhibitors and chemoradiation in stage III unresectable non-small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2019 Aug;134:259-267. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.05.027. Epub 2019 May 29. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31319991 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic, Inflammatory, and Molecular Impact of Cancer Cachexia on the Liver.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 7;25(22):11945. doi: 10.3390/ijms252211945. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596015 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bradley JD, et al. Long-term results of nrg oncology RTOG 0617: standard- versus high-dose chemoradiotherapy with or without cetuximab for unresectable stage iii non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol.: Offic. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2020;38:706–714. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.01162. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Girard N, et al. Treatment characteristics and real-world progression-free survival in patients with unresectable stage III NSCLC who received durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy: findings from the PACIFIC-R study. J. Thorac. Oncol. Offic. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer. 2023;18:181–193. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

