Low Vitamin D Levels in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroparesis: Relationships with Nausea and Vomiting, Gastric Emptying and Gastric Myoelectrical Activity
- PMID: 38877334
- PMCID: PMC11341680
- DOI: 10.1007/s10620-024-08520-8
Low Vitamin D Levels in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroparesis: Relationships with Nausea and Vomiting, Gastric Emptying and Gastric Myoelectrical Activity
Abstract
Patients with gastroparesis (Gp) often have diets deficient in calories, electrolytes, and vitamins. Vitamin D levels have been reported to be low in some patients with Gp but has not been systematically studied.
Aims: To determine vitamin D levels and relationships among symptoms, gastric emptying and gastric myoelectrical activity (GMA) in patients with symptoms of Gp.
Methods: 25-hydroxy-vitamin D was measured in patients at enrollment in the Gastroparesis Clinical Consortium Registry. Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptoms Index (GCSI), gastric emptying, and GMA before and after water load satiety test (WLST) were measured. GMA, expressed as percentage distribution of activity in normal and dysrhythmic ranges, was recorded using electrogastrography.
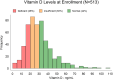
Results: Overall, vitamin D levels were low (< 30 ng/ml) in 288 of 513 (56.1%) patients with symptoms of Gp (206 of 376 (54.8%) patients with delayed gastric emptying (Gp) and 82 of 137 (59.9%) patients with symptoms of Gp and normal gastric emptying). Low vitamin D levels were associated with increased nausea and vomiting (P < 0.0001), but not with fullness or bloating subscores. Low vitamin D levels in patients with Gp were associated with greater meal retention at four hours (36% retention) compared with Gp patients with normal vitamin D levels (31% retention; P = 0.05). Low vitamin D in patients with normal gastric emptying was associated with decreased normal 3 cpm GMA before (P = 0.001) and increased tachygastria after WLST (P = 0.01).
Conclusions: Low vitamin D levels are present in half the patients with symptoms of gastroparesis and are associated with nausea and vomiting and gastric neuromuscular dysfunction.
Keywords: Functional dyspepsia; Gastric dysrhythmias; Gastroparesis; Nausea and vomiting; Vitamin D deficiency.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Kenneth Koch is a shareholder in the 3CPM Company.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of endoscopic pyloric therapies for patients with nausea and vomiting and functional obstructive gastroparesis.Auton Neurosci. 2017 Jan;202:56-61. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2016.07.004. Epub 2016 Jul 16. Auton Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 27460691
-
Gastric myoelectrical activity based AI-derived threshold predicts resolution of gastroparesis post-pyloric balloon dilation.Surg Endosc. 2023 Mar;37(3):1789-1798. doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09642-8. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Surg Endosc. 2023. PMID: 36229558
-
Effect of liquid and solid test meals on symptoms and gastric myoelectrical activity in patients with gastroparesis and functional dyspepsia.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2023 Feb;35(2):e14376. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14376. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2023. PMID: 35411675 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical presentation and pathophysiology of gastroparesis.Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2015 Mar;44(1):21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2014.11.003. Epub 2015 Jan 5. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2015. PMID: 25667020 Review.
-
Gastroparesis Updates on Pathogenesis and Management.Gut Liver. 2017 Sep 15;11(5):579-589. doi: 10.5009/gnl16336. Gut Liver. 2017. PMID: 28535580 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Case Report: Atypical presentation of rickets with hypocalcemia-related emesis.Front Pediatr. 2025 Jul 31;13:1627190. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1627190. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40822694 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pasricha PJ, Colvin R, Yakes K, Hasler WL, Abell TL, Unalp-Arida A, Nguyen L, Farrugia G, Koch KL, Parkman HP, Snape WJ, Lee L, Tonascia J, Hamilton FA. Clinical characteristics of patients with chronic unexplained nausea and vomiting and normal gastric emptying. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;7:567–576.10.1016/j.cgh.2011.03.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pasricha PJ, Grover M, Yates KP, Abell TL, Bernard CE, Koch KL, McCallum RW, Sarosiek I, Kuo B, Bulat R, Chen J, Shulman RJ, Lee L, Tonascia J, Miriel LA, Hamilton F, Farrugia G, Parkman HP. Functional dyspepsia and gastroparesis in tertiary care are interchangeable syndromes with common clinical and pathological features. Gastroenterology 2021;160:2006–2017. 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.01.230 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U24 DK074008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK074008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK074007/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK112193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK074007/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK073975/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK074035/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000424/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK074035/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK073983/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK073974/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK112194/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK073983/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK112193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24DK074008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000424/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK073975/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK073974/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical