Impaired angiotensin II signaling in septic shock
- PMID: 38877367
- PMCID: PMC11178728
- DOI: 10.1186/s13613-024-01325-y
Impaired angiotensin II signaling in septic shock
Abstract
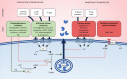
Recent years have seen a resurgence of interest for the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in critically ill patients. Emerging data suggest that this vital homeostatic system, which plays a crucial role in maintaining systemic and renal hemodynamics during stressful conditions, is altered in septic shock, ultimately leading to impaired angiotensin II-angiotensin II type 1 receptor signaling. Indeed, available evidence from both experimental models and human studies indicates that alterations in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system during septic shock can occur at three distinct levels: 1. Impaired generation of angiotensin II, possibly attributable to defects in angiotensin-converting enzyme activity; 2. Enhanced degradation of angiotensin II by peptidases; and/or 3. Unavailability of angiotensin II type 1 receptor due to internalization or reduced synthesis. These alterations can occur either independently or in combination, ultimately leading to an uncoupling between the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system input and downstream angiotensin II type 1 receptor signaling. It remains unclear whether exogenous angiotensin II infusion can adequately address all these mechanisms, and additional interventions may be required. These observations open a new avenue of research and offer the potential for novel therapeutic strategies to improve patient prognosis. In the near future, a deeper understanding of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system alterations in septic shock should help to decipher patients' phenotypes and to implement targeted interventions.
Keywords: Angiotensin II; Angiotensin-converting enzyme; Circulatory failure; Dipeptidyl peptidase 3; Neprilysin; Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system; Sepsis; Septic shock.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The Cardiovascular Markers in Stress Conditions (MASCOT) Research Group is supported by a research grant from 4TEEN4 Pharmaceuticals GmbH, which allowed salary support for two co-authors (AP, MG). AM received speaker’s honoraria from Abbott, Novartis, Orion, Roche, and Servier, and fees as a member of the advisory board and/or steering committee from Cardiorentis, Adrenomed, MyCartis, Neurotronik, and Sphingotec. PP received travel and consultancy reimbursement from Adrenomed, SphingoTec, 4TEEN4, AM-Pharma, Baxter, and EBI. The remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Schweda F, Kurtz A. Regulation of renin release by local and systemic factors. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2011;161:1–44. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

