S100A6 Regulates nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway: an in vitro and in vivo study
- PMID: 38877413
- PMCID: PMC11179208
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-024-00853-4
S100A6 Regulates nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway: an in vitro and in vivo study
Abstract
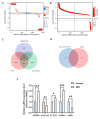
Background: Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) is a common musculoskeletal degenerative disease, which often leads to low back pain and even disability, resulting in loss of labor ability and decreased quality of life. Although many progresses have been made in the current research, the underlying mechanism of IDD remains unclear. The apoptosis of nucleus pulposus (NP) cells (NPCs) is an important pathological mechanism in intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD). This study evaluated the relationship between S100A6 and NPCs and its underlying mechanism.
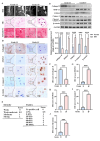
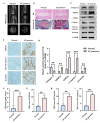
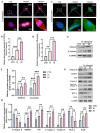
Methods: Mass spectrometry, bioinformatics, and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analyses were used to screen and verify hub genes for IDD in human IVD specimens with different degeneration degrees. Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and/or immunofluorescence (IF) were used to detect the expression level of S100A6 in human NP tissues and NPCs. The apoptotic phenotype of NPCs and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway were evaluated using flow cytometry, western blotting, and IF. S100A6 was overexpressed or knocked down in NPCs to determine its impact on apoptosis and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway activity. Moreover, we used the XAV-939 to inhibit and SKL2001 to activate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. The therapeutic effect of S100A6 inhibition on IDD was also evaluated.
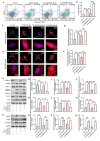
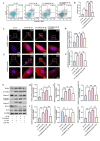
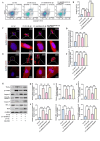
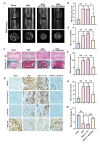
Results: S100A6 expression increased in IDD. In vitro, increased S100A6 expression promoted apoptosis in interleukin (IL)-1β-induced NPCs. In contrast, the inhibition of S100A6 expression partially alleviated the progression of annulus fibrosus (AF) puncture-induced IDD in rats. Mechanistic studies revealed that S100A6 regulates NPC apoptosis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Conclusions: This study showed that S100A6 expression increased during IDD and promoted NPCs apoptosis by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, suggesting that S100A6 is a promising new therapeutic target for IDD.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Intervertebral disc degeneration; S100A6; Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wharton's Jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells suppress apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells in intervertebral disc degeneration via Wnt pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Oct;24(19):9807-9814. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202010_23190. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33090383
-
SKI knockdown suppresses apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation of nucleus pulposus cells via inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and ameliorates disc degeneration.Apoptosis. 2022 Feb;27(1-2):133-148. doi: 10.1007/s10495-022-01707-2. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Apoptosis. 2022. PMID: 35147801
-
Role of LncRNA TUG1 in intervertebral disc degeneration and nucleus pulposus cells via regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Sep 23;491(3):668-674. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.07.146. Epub 2017 Jul 26. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28756222
-
Targeting nucleus pulposus cell death in the treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration.JOR Spine. 2024 Dec 18;7(4):e70011. doi: 10.1002/jsp2.70011. eCollection 2024 Dec. JOR Spine. 2024. PMID: 39703198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Microvascular Variations in the Process of Intervertebral Disk Degeneration and Its Regulatory Mechanisms: A Literature Review.Orthop Surg. 2024 Nov;16(11):2587-2597. doi: 10.1111/os.14209. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Orthop Surg. 2024. PMID: 39205477 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Scar-associated macrophages and biliary epithelial cells interaction exacerbates hepatic fibrosis in biliary atresia.Pediatr Res. 2025 May 18. doi: 10.1038/s41390-025-04100-2. Online ahead of print. Pediatr Res. 2025. PMID: 40383871
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Induced by Propionibacterium acnes.Biomed Res Int. 2025 Apr 15;2025:5513856. doi: 10.1155/bmri/5513856. eCollection 2025. Biomed Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40264644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting skeletal interoception: a novel mechanistic insight into intervertebral disc degeneration and pain management.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Feb 12;20(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05577-7. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 39940003 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boom A, Pochet R, Authelet M, Pradier L, Borghgraef P, Van Leuven F, Heizmann CW, Brion JP. Astrocytic calcium/zinc binding protein S100A6 over expression in Alzheimer’s disease and in PS1/APP transgenic mice models. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1742:161–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.09.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cai Z, Luo Q, Yang X, Pu L, Zong H, Shi R, He P, Xu Y, Li Y, Zhang J. Overloaded axial stress activates the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway in nucleus pulposus cells of adult degenerative scoliosis combined with intervertebral disc degeneration. Mol Biol Rep. 2023;50:4791–98. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08390-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Xie JJ, Jin MY, Gu YT, Wu CC, Guo WJ, Yan YZ, Zhang ZJ, Wang JL, Zhang XL, Lin Y, Sun JL, Zhu GH, Wang XY, Wu YS. Sirt6 overexpression suppresses senescence and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells by inducing autophagy in a model of intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:56. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0085-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

