Offsetting pb induced oxidative stress in Vicia faba plants by foliar spray of chitosan through adjustment of morpho-biochemical and molecular indices
- PMID: 38877427
- PMCID: PMC11177494
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-024-05227-w
Offsetting pb induced oxidative stress in Vicia faba plants by foliar spray of chitosan through adjustment of morpho-biochemical and molecular indices
Abstract
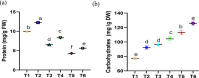
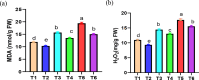
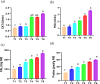
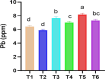
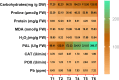
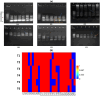
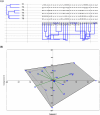
In the course of their life, plants face a multitude of environmental anomaly that affects their growth and production. In recent decades, lead (Pb) gained an increasing attention as it is among the most significant contaminants in the environment. Therefore, in this study the effects of Pb concentrations (0, 50 and 100 ppm) on Vicia faba plants and attempts to alleviate this stress using chitosan (Chs; 0 and 0.1%) were performed. The results validated that with increasing Pb concentrations, a decline in growth, pigments and protein contents was observed. In the same time, a significant upsurge in the stress markers, both malondialdehyde (MDA) and H2O2, was observed under Pb stress. Nonetheless, foliar spraying with Chs improves the faba bean growth, pigment fractions, protein, carbohydrates, reduces MDA and H2O2 contents and decreases Pb concentrations under Pb stress. Pb mitigation effects by Chs are probably related with the activity of antioxidant enzymes, phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) and proline. The application of Chs enhanced the activities of peroxidase, catalase and PAL by 25.77, 17.71 and 20.07%, respectively at 100 ppm Pb compared to their control. Plant genomic material exhibits significant molecular polymorphism, with an average polymorphism of 91.66% across all primers. To assess the genetic distance created among treatments, the dendrogram was constructed and the results of the similarity index ranged from 0.75 to 0.95, indicating genetic divergence. Our research offers a thorough comprehension of the role of Chs in lessening the oxidative stress, which will encourage the use of Chs in agricultural plant protection.
Keywords: Vicia faba; Antioxidant; Chitosan; ISSR marker; Lead stress; Oxidative stress; Phenylalanine ammonia lyase.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Experimental research and field studies on plants: "All relevant institutional, national and international guidelines and legislation were compiled or adhered to in the production of this study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes aggravated biochemical and subcellular damages in leaves of broad bean (Vicia faba L.) seedlings under combined stress of lead and cadmium.J Hazard Mater. 2014 Jun 15;274:404-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.04.036. Epub 2014 Apr 25. J Hazard Mater. 2014. PMID: 24806869
-
The influence of selenium on root growth and oxidative stress induced by lead in Vicia faba L. minor plants.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2012 Jun;147(1-3):320-8. doi: 10.1007/s12011-011-9292-6. Epub 2011 Dec 10. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2012. PMID: 22161289
-
Green synthesis of a dual-functional sulfur nanofertilizer to promote growth and enhance salt stress resilience in faba bean.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Jun 26;24(1):607. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05270-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38926889 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative and molecular responses in Capsicum annuum L. after hydrogen peroxide, salicylic acid and chitosan foliar applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 May 15;14(5):10178-96. doi: 10.3390/ijms140510178. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23676352 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of calcium and potassium on antioxidant system of Vicia faba L. Under cadmium stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(6):6604-6619. doi: 10.3390/ijms13066604. Epub 2012 May 29. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22837652 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Interpreting the potential of biogenic TiO2 nanoparticles on enhancing soybean resilience to salinity via maintaining ion homeostasis and minimizing malondialdehyde.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 15;15(1):12904. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-94421-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40234514 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigating drought stress and enhancing maize resistance through biopriming with Rhizopus arrhizus: insights into Morpho-Biochemical and molecular adjustments.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jun 11;25(1):779. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06793-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40500725 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptability assessment of Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus terreus isolated from long-term municipal/industrial effluent-irrigated soils to cadmium stress.BMC Microbiol. 2025 May 15;25(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s12866-025-04000-9. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40375089 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang Y, Hu J, Bai J, Wang J, Yin R, Wang J, Lin X. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alleviate the heavy metal toxicity on sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) plants cultivated on a heavily contaminated field soil at a WEEE-recycling site. Sci Total Environ. 2018;282–90. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.331. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

