Evaluating the effectiveness of combined T4 and T3 therapy or desiccated thyroid versus T4 monotherapy in hypothyroidism: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38877429
- PMCID: PMC11177353
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-024-01612-6
Evaluating the effectiveness of combined T4 and T3 therapy or desiccated thyroid versus T4 monotherapy in hypothyroidism: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Persistent symptoms in hypothyroid patients despite normalized TSH levels suggest the need for alternative treatments. This study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of combined T4 and T3 therapy or desiccated thyroid (DTE) compared to T4 monotherapy, with a focus on thyroid profile, lipid profile, and quality of life metrics.
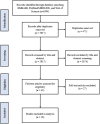
Methods: We conducted a systematic review in Embase, Medline/PubMed, and Web of Science up to 11/23/2023. We used the following keywords: "Armour Thyroid," OR "Thyroid extract," OR "Natural desiccated thyroid," OR "Nature-Throid," "desiccated thyroid," OR "np thyroid," OR "Synthroid," OR "levothyroxine," OR "Liothyronine," "Cytomel," OR "Thyroid USP," OR "Unithroid." AND "hypothyroidism. " We only included RCTs and excluded non-RCT, case-control studies, and non-English articles.
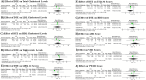
Results: From 6,394 identified records, 16 studies qualified after screening and eligibility checks. We included two studies on desiccated thyroid and 15 studies on combined therapy. In this meta-analysis, combination therapy with T4 + T3 revealed significantly lower Free T4 levels (mean difference (MD): -0.34; 95% CI: -0.47, -0.20), Total T4 levels (mean difference: -2.20; 95% CI: -3.03, -1.37), and GHQ-28 scores (MD: -2.89; 95% CI: -3.16, -2.63), compared to T4 monotherapy. Total T3 levels were significantly higher in combined therapy (MD: 29.82; 95% CI: 22.40, 37.25). The analyses demonstrated moderate to high heterogeneity. There was no significant difference in Heart Rate, SHBG, TSH, Lipid profile, TSQ-36, and BDI Score. Subjects on DTE had significantly higher serum Total T3 levels (MD: 50.90; 95% CI: 42.39, 59.42) and significantly lower serum Total T4 (MD: -3.11; 95% CI: -3.64, -2.58) and Free T4 levels (MD: -0.50; 95% CI: -0.57, -0.43) compared to T4 monotherapy. Moreover, DTE treatment showed modestly higher TSH levels (MD: 0.49; 95% CI: 0.17, 0.80). The analyses indicated low heterogeneity. There was no significant difference in Heart Rate, SHBG, Lipid profile, TSQ-36, GHQ-28, and BDI Score.
Conclusions: Our study revealed that combined therapy and DTE lead to higher T3 and lower T4 levels, compared to T4 monotherapy in hypothyroidism. However, no significant effects on heart rate, lipid profile, or quality of life were noted. Given the heterogeneity of results, personalized treatment approaches are recommended.
Keywords: Desiccated thyroid extract; Hypothyroidism; Levothyroxine; Liothyronine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Comparative Effectiveness of Levothyroxine, Desiccated Thyroid Extract, and Levothyroxine+Liothyronine in Hypothyroidism.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Oct 21;106(11):e4400-e4413. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab478. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34185829 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment Preferences in Patients With Hypothyroidism.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025 Feb 18;110(3):887-900. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgae651. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025. PMID: 39290156
-
Liothyronine and Desiccated Thyroid Extract in the Treatment of Hypothyroidism.Thyroid. 2020 Oct;30(10):1399-1413. doi: 10.1089/thy.2020.0153. Epub 2020 May 12. Thyroid. 2020. PMID: 32279609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thyroxine alone or thyroxine plus triiodothyronine replacement therapy for hypothyroidism.Nucl Med Commun. 2009 Aug;30(8):586-93. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0b013e32832c79e0. Nucl Med Commun. 2009. PMID: 19491714
-
Daily Administration of Short-Acting Liothyronine Is Associated with Significant Triiodothyronine Excursions and Fails to Alter Thyroid-Responsive Parameters.Thyroid. 2016 Jun;26(6):770-8. doi: 10.1089/thy.2015.0629. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Thyroid. 2016. PMID: 27030088 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
LT4/LT3 Combination Therapy vs. Monotherapy with LT4 for Persistent Symptoms of Hypothyroidism: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 25;25(17):9218. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179218. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273168 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical thyroidology: beyond the 1970s' TSH-T4 Paradigm.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 24;16:1529791. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1529791. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40630099 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wojtachnio D, Osiejewska A, Bartoszewicz J, Grądzik A, Nowakowska I, Kudan M, Gorajek A, Mikut K. Hypothyroidism: clinical presentation, diagnosis, treatment. J Educ Health Sport. 2022;12:650–660. doi: 10.12775/jehs.2022.12.08.067. - DOI
-
- Baraka B, Abosheaishaa H, Nassar M. Immunotherapy-induced thyroid dysfunction: an updated review. Egypt J Int Med. 2023;35:48. doi: 10.1186/s43162-023-00210-7. - DOI
-
- Bjerkreim BA, Hammerstad SS, Gulseth HL, Berg TJ, Lee-Odegard S, Eriksen EF. Thyroid Signaling Biomarkers in Female Symptomatic Hypothyroid Patients on Liothyronine versus Levothyroxine Monotherapy: A Randomized Crossover Trial. J Thyroid Res. 2022;2022:6423023. doi: 10.1155/2022/6423023. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

