Global distribution of zoonotic digenetic trematodes: a scoping review
- PMID: 38877531
- PMCID: PMC11177464
- DOI: 10.1186/s40249-024-01208-1
Global distribution of zoonotic digenetic trematodes: a scoping review
Abstract
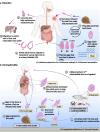
Background: Digenetic trematodes, including blood flukes, intestinal flukes, liver flukes, lung flukes, and pancreatic flukes, are highly diverse and distributed widely. They affect at least 200 million people worldwide, so better understanding of their global distribution and prevalence are crucial for controlling and preventing human trematodiosis. Hence, this scoping review aims to conduct a comprehensive investigation on the spatio-temporal distribution and epidemiology of some important zoonotic digenetic trematodes.
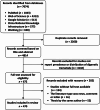
Methods: We conducted a scoping review by searching PubMed, Web of Science, Google Scholar, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, and Wanfang databases for articles, reviews, and case reports of zoonotic digenetic trematodes, without any restrictions on the year of publication. We followed the inclusion and exclusion criteria to identify relevant studies. And relevant information of the identified studies were collected and summarized.
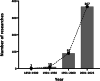
Results: We identified a total of 470 articles that met the inclusion criteria and were included in the review finally. Our analysis revealed the prevalence and global distribution of species in Schistosoma, Echinostoma, Isthmiophora, Echinochasmus, Paragonimus, Opisthorchiidae, Fasciolidae, Heterophyidae, and Eurytrema. Although some flukes are distributed worldwide, developing countries in Asia and Africa are still the most prevalent areas. Furthermore, there were some overlaps between the distribution of zoonotic digenetic trematodes from the same genus, and the prevalence of some zoonotic digenetic trematodes was not entirely consistent with their global distribution. The temporal disparities in zoonotic digenetic trematodes may attribute to the environmental changes. The gaps in our knowledge of the epidemiology and control of zoonotic digenetic trematodes indicate the need for large cohort studies in most countries.
Conclusions: This review provides important insights into the prevalence and global distribution of some zoonotic digenetic trematodes, firstly reveals spatio-temporal disparities in these digenetic trematodes. Countries with higher prevalence rate could be potential sources of transmitting diseases to other areas and are threat for possible outbreaks in the future. Therefore, continued global efforts to control and prevent human trematodiosis, and more international collaborations are necessary in the future.
Keywords: Digenetic trematode; Epidemiology; Spatio-temporal distribution.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epidemiology and Geographical Distribution of Human Trematode Infections.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1454:443-505. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-60121-7_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39008273 Review.
-
Global status of fish-borne zoonotic trematodiasis in humans.Acta Parasitol. 2013 Sep;58(3):231-58. doi: 10.2478/s11686-013-0155-5. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Acta Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 23990419 Review.
-
Epidemiology of Trematode Infections: An Update.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1154:359-409. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-18616-6_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31297768
-
Insights on foodborne zoonotic trematodes in freshwater snails in North and Central Vietnam.Parasitol Res. 2021 Mar;120(3):949-962. doi: 10.1007/s00436-020-07027-1. Epub 2021 Jan 10. Parasitol Res. 2021. PMID: 33426572
-
Towards improved diagnosis of zoonotic trematode infections in Southeast Asia.Adv Parasitol. 2010;73:171-95. doi: 10.1016/S0065-308X(10)73007-4. Adv Parasitol. 2010. PMID: 20627143 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring glutathione transferase and Cathepsin L-like proteinase for designing of epitopes-based vaccine against Fasciola hepatica by immunoinformatics and biophysics studies.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 26;15:1478107. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1478107. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39391319 Free PMC article.
-
Establishing a predictive model for liver fluke infection on the basis of early changes in laboratory indicators: a retrospective study.Parasit Vectors. 2025 May 22;18(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s13071-025-06833-9. Parasit Vectors. 2025. PMID: 40405253 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional and national disease burden of food-borne trematodiases: projections to 2030 based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Infect Dis Poverty. 2024 Dec 16;13(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s40249-024-01265-6. Infect Dis Poverty. 2024. PMID: 39676162 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marsden P. Clinicai Parasitology, 9th Editon, Beaver PC, Jung RC, Cupp EW. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, 1984. Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropical. 1984;17:219.
-
- Doughty BL. Schistosomes and Other Trematodes. In: Baron S, editor. Medical Microbiology. 4. Galveston (TX): University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston; 1996. - PubMed
-
- Galaktionov KV, Dobrovolskij AA. In: Fried B, Graczyk TK, editors. The Biology and Evolution of Trematodes. Springer Netherlands; 2003. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/257234158_Galaktionov_K_V_A_A_D....
-
- Crotti M. Digenetic Trematodes: an existence as .parasites Brief general overview. Microbiol Med. 2013;28(2):97–101. doi: 10.4081/mm.2013.2256. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- NPRC-2019-194-30/National Parasitic Resources Center of China
- 2021YFC2300800/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2021YFC2300801/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 82072303/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 22qntd4804/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Sun Yat-sen University
- 2022NHCTDCKFKT11003/Open Foundation of NHC Key Laboratory of Tropical Disease Control, Hainan Medical University
- YSPTZX202133/Specific Research Fund of the Innovation Platform for Academicians of Hainan Province
- ZDYF2020120/the Key Research and Development Program of Hainan Province
- ZDKJ202003/the Major Science and Technology Program of Hainan Province
- ZDKJ2021035/the Major Science and Technology Program of Hainan Province
- 2020TTM007/the Open Foundation of Key Laboratory of Tropical Translational Medicine of Ministry of Education, Hainan Medical University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

