The advanced lung cancer inflammation index (ALI) predicted the postoperative survival rate of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and the construction of a nomogram model
- PMID: 38877553
- PMCID: PMC11177447
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-024-03432-3
The advanced lung cancer inflammation index (ALI) predicted the postoperative survival rate of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and the construction of a nomogram model
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the prognostic significance of the advanced lung cancer inflammation index (ALI) in patients with operable non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). By constructing the nomogram model, it can provide a reference for clinical work.
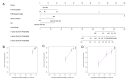
Methods: A total of 899 patients with non-small cell lung cancer who underwent surgery in our hospital between January 2017 and June 2021 were retrospectively included. ALI was calculated by body mass index (BMI) × serum albumin/neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR). The optimal truncation value of ALI was obtained using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and divided into two groups. Survival analysis was represented by the Kaplan-Meier curve. The predictors of Overall survival (OS) were evaluated by the Cox proportional risk model using single factor and stepwise regression multifactor analysis. Based on the results of multi-factor Cox proportional risk regression analysis, a nomogram model was established using the R survival package. The bootstrap method (repeated sampling 1 000 times) was used for internal verification of the nomogram model. The concordance index (C-index) was used to represent the prediction performance of the nomogram model, and the calibration graph method was used to visually represent its prediction conformity. The application value of the model was evaluated by decision curve analysis (DCA).
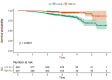
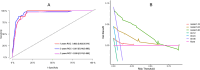
Results: The optimal cut-off value of ALI was 70.06, and the low ALI group (ALI < 70.06) showed a poor survival prognosis. In multivariate analyses, tumor location, pathological stage, neuroaggression, and ALI were independently associated with operable NSCLC-specific survival. The C index of OS predicted by the nomogram model was 0.928 (95% CI: 0.904-0.952). The bootstrap self-sampling method (B = 1000) was used for internal validation of the prediction model, and the calibration curve showed good agreement between the prediction and observation results of 1-year, 2-year, and 3-year OS. The ROC curves for 1-year, 2-year, and 3-year survival were plotted according to independent factors, and the AUC was 0.952 (95% CI: 0.925-0.979), 0.951 (95% CI: 0.916-0.985), and 0.939 (95% CI: 0.913-0.965), respectively. DCA shows that this model has good clinical application value.
Conclusion: ALI can be used as a reliable indicator to evaluate the prognosis of patients with operable NSCLC, and through the construction of a nomogram model, it can facilitate better individualized treatment and prognosis assessment.
Keywords: Advanced lung cancer inflammation index; Nomogram; Non-small cell lung cancer; Prognosis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al. Global Cancer Statistics. 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. 10.3322/caac.21660. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

