Efficacy and safety of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on prediabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 38877565
- PMCID: PMC11177512
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-024-01371-3
Efficacy and safety of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on prediabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Prediabetes is a condition preceding the development of diabetes and is associated with an increased risk of a number of complications. The primary mode of management is thought to be lifestyle modification. Pharmacological therapy, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs), were not well addressed in the literature and were only evaluated in trials as secondary and exploratory outcomes with a limited sample size. Here, GLP-1RAs are evaluated as a comprehensive therapy approach for patients with prediabetes.
Methods: A comprehensive search of Web of Science, SCOPUS, PubMed, and Cochrane was performed on May 5, 2023, to retrieve randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing the effect of GLP-1RAs to placebo and/or lifestyle modification on prediabetes reversion to normoglycemia, prevention of overt diabetes, glycemic control, anthropometric parameters, and lipid profiles. Review Manager (RevMan) version 5.4 was used. The quality of RCTs was assessed using the revised version of the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool. GRADE was performed to evaluate the certainty of evidence.
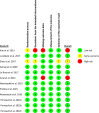
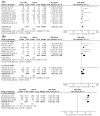
Results: Twelve trials involving 2903 patients in the GLP-1RAs group and 1413 in the control group were included in the meta-analysis. Low quality of evidence revealed that GLP-1RAs significantly increased the incidence of prediabetes reversion to the normoglycemic state [RR = 1.76, 95% CI (1.45, 2.13), P < 0.00001] and moderate quality of evidence showed that GLP-1RAs significantly prevented new-onset diabetes [RR = 0.28, 95% CI (0.19, 0.43), P < 0.00001]. Significant reductions in HbA1c, fasting plasma glucose, body weight, waist circumference, triglycerides, and LDL were observed in the GLP-1RAs arm (P < 0.05). However, higher incidences of gastrointestinal disorders were reported in the GLP-1RAs group (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: GLP-1RAs combined with lifestyle modification proved to be a more effective therapy for managing prediabetic patients than lifestyle modification alone, with a tolerable safety profile. Future guidelines should consider GLP-1RAs as an adjunct to lifestyle modification in the management of prediabetic patients to provide better management and improve treatment adherence.
Keywords: Diabetes; Impaired; Lifestyle; Liraglutide; Normoglycemia; Prediabetes; Regression; Reversion; Tolerance.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Organization WH, Federation ID. Definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and intermediate hyperglycaemia : report of a WHO/IDF consultation. Geneva: World Health Organization.
-
- Magliano DJ, Boyko EJ, committee IDA 10th edition scientific. IDF DIABETES ATLAS. International Diabetes Federation; 2021; 54–5.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

