Entorhinal vessel density correlates with phosphorylated tau and TDP-43 pathology
- PMID: 38877668
- PMCID: PMC11247684
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.13896
Entorhinal vessel density correlates with phosphorylated tau and TDP-43 pathology
Abstract
Introduction: The entorhinal cortex (EC) and perirhinal cortex (PC) are vulnerable to Alzheimer's disease. A triggering factor may be the interaction of vascular dysfunction and tau pathology.
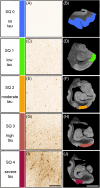
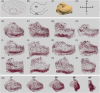
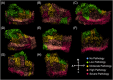
Methods: We imaged post mortem human tissue at 100 μm3 with 7 T magnetic resonance imaging and manually labeled individual blood vessels (mean = 270 slices/case). Vessel density was quantified and compared per EC subfield, between EC and PC, and in relation to tau and TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) semiquantitative scores.
Results: PC was more vascularized than EC and vessel densities were higher in posterior EC subfields. Tau and TDP-43 strongly correlated with vasculature density and subregions with severe tau at the preclinical stage had significantly greater vessel density than those with low tau burden.
Discussion: These data impact cerebrovascular maps, quantification of subfield vasculature, and correlation of vasculature and pathology at early stages. The ordered association of vessel density, and tau or TDP-43 pathology, may be exploited in a predictive context.
Highlights: Vessel density correlates with phosphorylated tau (p-tau) burden in entorhinal and perirhinal cortices. Perirhinal area 35 and posterior entorhinal cortex showed greatest p-tau burden but also the highest vessel density in the preclinical phase of Alzheimer's disease. We combined an ex vivo magnetic resonance imaging model and histopathology to demonstrate the 3D reconstruction of intracortical vessels and its spatial relationship to the pathology.
Keywords: intracortical; parahippocampal gyrus; perirhinal cortex; proximity; subfields; vasculature.
© 2024 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
A.V.D.K. has received royalties from Elsevier, has consulted and served on the medical advisory board for Nous Imaging and Turing Medical, has received travel support from Siemens Healthineers, and has stock options from Turing Medical. B.F. serves on the medical advisory board of DeepHealth/RadNet. B.F.’s interests were reviewed and are managed by Massachusetts General Hospital and Partners HealthCare in accordance with their conflict of interest policies. M.M. has served as a medicolegal consultant for and been paid for expert testimony by Cirinani Heller Harman law firm. M.P.F. has no relevant disclosures for this manuscript. J.C.A. has consulted Biospective, Inc. and received travel support from R01AG070592. J.L.R., J.O., E.R., and N.M. have no conflicts of interest to declare. A.V.D.K., B.F., M.M., M.P.F., and J.C.A.’s disclosures are unrelated to this work. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures




Similar articles
-
TDP-43 and tau concurrence in the entorhinal subfields in primary age-related tauopathy and preclinical Alzheimer's disease.Brain Pathol. 2023 Jul;33(4):e13159. doi: 10.1111/bpa.13159. Epub 2023 Apr 10. Brain Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37037195 Free PMC article.
-
Association of quantitative histopathology measurements with antemortem medial temporal lobe cortical thickness in the Alzheimer's disease continuum.Acta Neuropathol. 2024 Sep 3;148(1):37. doi: 10.1007/s00401-024-02789-9. Acta Neuropathol. 2024. PMID: 39227502 Free PMC article.
-
CSF tau and the CSF tau/ABeta ratio for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 22;3(3):CD010803. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010803.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28328043 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropathological hallmarks in the post-mortem retina of neurodegenerative diseases.Acta Neuropathol. 2024 Aug 19;148(1):24. doi: 10.1007/s00401-024-02769-z. Acta Neuropathol. 2024. PMID: 39160362 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional Tasks and an Energy Crisis are Crucial Players in Determining the Vulnerability of the Entorhinal Cortex to Early Damage in Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2024;21(5):295-311. doi: 10.2174/0115672050324909240823104209. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2024. PMID: 39279693 Review.
Cited by
-
Visualizing cortical laminar architecture in the living human brain using next-generation ultra-high-gradient diffusion MRI.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 10:rs.3.rs-6724971. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-6724971/v1. Res Sq. 2025. PMID: 40585214 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Elevated TDP-43 serum levels associated with postoperative delirium following major cardiac surgery.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025 Mar 7;45:100974. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2025.100974. eCollection 2025 May. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025. PMID: 40134937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duvernoy H, Cabanis EA, Bourgouin P, Risold PY. The Human Parahippocampus: Functional Anatomy, Vascularization and Serial Sections With MRI. Springer; 1998.
-
- Marinković SV, Milisavljević MM, Vučković VD. Experimental and clinical studies: microvascular anatomy of the uncus and the parahippocampal gyrus. Neurosurgery. 1991;29:805. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

