Unlocking the potential of robotic-assisted bronchoscopy: overcoming challenging anatomy and locations
- PMID: 38877690
- PMCID: PMC11179493
- DOI: 10.1177/17534666241259369
Unlocking the potential of robotic-assisted bronchoscopy: overcoming challenging anatomy and locations
Abstract
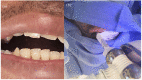
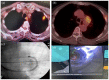
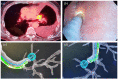
Robotic-assisted bronchoscopy (RAB) was recently added to the armamentarium of tools used in sampling peripheral lung nodules. Protocols and guidelines have since been published advocating use of large oral artificial airways, use of confirmatory technologies such as radial endobronchial ultrasound (R-EBUS), and preferably limiting sampling to pulmonary parenchymal lesions. We present three clinical cases where RAB was used unconventionally to sample pulmonary nodules in unusual locations and in patients with challenging airway anatomy. In case 1, we introduced the ion catheter through a nasal airway in a patient with trismus. In case 2, we established a diagnosis by sampling a station 5 lymph node, and in case 3, we sampled a lesion located behind an airway stump from previous thoracic surgery. All three patients would have presented significant challenges for alternative biopsy modalities such as CT-guided needle biopsy or video-assisted thoracic surgery.
Keywords: biopsy; bronchoscopy; robotic bronchoscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ali MS, Ghori UK, Wayne MT, et al.. Diagnostic performance and safety profile of robotic-assisted bronchoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Am Thorac Soc 2023; 20: 1801–1812. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

