Patients taking benralizumab, dupilumab, or mepolizumab have lower postvaccination SARS-CoV-2 immunity
- PMID: 38878020
- PMCID: PMC11305925
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2024.03.029
Patients taking benralizumab, dupilumab, or mepolizumab have lower postvaccination SARS-CoV-2 immunity
Abstract
Background: Biologic therapies inhibiting the IL-4 or IL-5 pathways are very effective in the treatment of asthma and other related conditions. However, the cytokines IL-4 and IL-5 also play a role in the generation of adaptive immune responses. Although these biologics do not cause overt immunosuppression, their effect in primary severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) immunization has not been studied completely.
Objective: Our aim was to evaluate the antibody and cellular immunity after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination in patients on biologics (PoBs).
Methods: Patients with severe asthma or atopic dermatitis who were taking benralizumab, dupilumab, or mepolizumab and had received the initial dose of the 2-dose adult SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine were enrolled in a prospective, observational study. As our control group, we used a cohort of immunologically healthy subjects (with no significant immunosuppression) who were not taking biologics (NBs). We used a multiplexed immunoassay to measure antibody levels, neutralization assays to assess antibody function, and flow cytometry to quantitate Spike-specific lymphocytes.
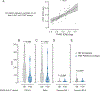
Results: We analyzed blood from 57 patients in the PoB group and 46 control subjects from the NB group. The patients in the PoB group had lower levels of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, pseudovirus neutralization, live virus neutralization, and frequencies of Spike-specific B and CD8 T cells at 6 months after vaccination. In subgroup analyses, patients with asthma who were taking biologics had significantly lower pseudovirus neutralization than did subjects with asthma who were not taking biologics.
Conclusion: The patients in the PoB group had reduced SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody titers, neutralizing activity, and virus-specific B- and CD8 T-cell counts. These results have implications when considering development of a more individualized immunization strategy in patients who receive biologic medications blocking IL-4 or IL-5 pathways.
Keywords: Asthma biologics; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antibody neutralization; benralizumab; dupilumab; mRNA vaccines; memory B cells; memory T cells; mepolizumab.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure statement Supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) (grants NIH/NHLBI T32HL116271 [to M.C.R., P.A.L., and N.S.]; the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the NIH (UL1TR002378 [to N.S.]; P01AI125180 [to I.S. and F.E.L.]; U54CA260563 [to I.S. and F.E.L.]; R01AI121252 [to F.E.L.]; R01AI172254 [to F.E.L.]; U01AI141993 [to F.E.L.]; and NIH P51OD011132, 1U54CA260563, and the NIH/NIAID Centers of Excellence for Influenza Research and Response (under contract 75N93021C00017 to Emory University). This work does not necessarily represent the views of the US government or Department of Veterans Affairs. Disclosure of potential conflict of interest: N. S. Haddad is employed by MicroB-plex, Inc, but did not receive any payments for this article. C. Swenson receives compensation and consulting fees from Insmed, Inc, that are unrelated to this article. F. Holguin is a member of the adjudication committee of the ASPEN (A Study to Assess the Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Brensocatib in Participants With Non-Cystic Fibrosis Bronchiectasis) trial at Insmed, Inc. J. D. Roback received funding from an NIH grant in the past 36 months. I. Sanz receives royalties from BLI INC for plasma cell survival media; consulting fees from GSK, Pfizer, Kayverna, Johnson & Johnson, Celgene, Bristol-Myer Squibb, and Visterra; and honoraria for presentations from Yale and Harvard Universities. In addition, I. Sanz has a patent on plasma cell survival media. F. Eun-Hyung Lee receives or has received research grants from Genentech and the Gates Foundation; royalties from BLI INC for plasma cell survival media; consulting fees from Be Bio Pharma; honoraria for presentations at the University of Pennsylvania, the University of Cincinnati, and the Gerontological Advanced Practice Nurses Association; has patents on plasma cell survival media and media of elaborated newly synthesized antibodies (MENSA); and is the founder and owner of MicroB-plex, Inc. The rest of the authors declare that they have no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures
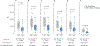
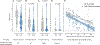


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

