Therapeutic perspectives on PDE4B inhibition in adipose tissue dysfunction and chronic liver injury
- PMID: 38878273
- PMCID: PMC11305103
- DOI: 10.1080/14728222.2024.2369590
Therapeutic perspectives on PDE4B inhibition in adipose tissue dysfunction and chronic liver injury
Abstract
Introduction: Chronic liver disease (CLD) is a complex disease associated with profound dysfunction. Despite an incredible burden, the first and only pharmacotherapy for metabolic-associated steatohepatitis was only approved in March of this year, indicating a gap in the translation of preclinical studies. There is a body of preclinical work on the application of phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors in CLD, none of these molecules have been successfully translated into clinical use.
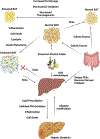
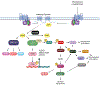
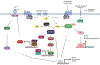
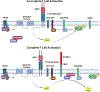
Areas covered: To design therapies to combat CLD, it is essential to consider the dysregulation of other tissues that contribute to its development and progression. As such, proper therapies must combat this throughout the body rather than focusing only on the liver. To detail this, literature characterizing the pathogenesis of CLD was pulled from PubMed, with a particular focus placed on the role of PDE4 in inflammation and metabolism. Then, the focus is shifted to detailing the available information on existing PDE4 inhibitors.
Expert opinion: This review gives a brief overview of some of the pathologies of organ systems that are distinct from the liver but contribute to disease progression. The demonstrated efficacy of PDE4 inhibitors in other human inflammatory diseases should earn them further examination for the treatment of CLD.
Keywords: Adipose; alcohol; chronic liver disease; liver fibrosis; obesity; phosphodiesterase.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest
The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
NIH Consensus Statement on Management of Hepatitis C: 2002.NIH Consens State Sci Statements. 2002 Jun 10-12;19(3):1-46. NIH Consens State Sci Statements. 2002. PMID: 14768714
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Elective high frequency oscillatory ventilation versus conventional ventilation for acute pulmonary dysfunction in preterm infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(4):CD000104. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000104. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jul 18;(3):CD000104. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000104.pub2. PMID: 14583909 Updated.
Cited by
-
Targeting Phosphodiesterase 4 in Gastrointestinal and Liver Diseases: From Isoform-Specific Mechanisms to Precision Therapeutics.Biomedicines. 2025 May 23;13(6):1285. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061285. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Azaindole Compounds as Phosphodiesterase 4B Inhibitors for Treating Immune-Inflammatory Diseases or Disorders.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2025 Apr 7;16(5):717-718. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.5c00158. eCollection 2025 May 8. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2025. PMID: 40365387
References
-
- Asrani SK, Devarbhavi H, Eaton J, et al. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J Hepatol. 2019. Jan;70(1):151–171. - PubMed
-
- Stepanova M, De Avila L, Afendy M, Younossi I, Pham H, and Cable R. Direct and Indirect Economic Burden of Chronic Liver Disease in the United States. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2016. July 24, 2016;15(5):759–766. - PubMed
-
- Gholam PM, Kotler DP, Flancbaum LJ. Liver Pathology in Morbidly Obese Patients Undergoing Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery. Obesity Surgery. 2002 2002/February/01;12(1):49–51. - PubMed
-
- Hilden M, Christoffersen P, Juhl E, et al. Liver Histology in a ‘Normal’ Population—Examinations of 503 Consecutive Fatal Traffic Casualties. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology. 1977. 1977/07/01;12(5):593–597. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
