Network enrichment significance testing in brain-phenotype association studies
- PMID: 38878300
- PMCID: PMC11179683
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.26714
Network enrichment significance testing in brain-phenotype association studies
Abstract
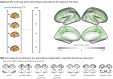
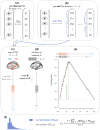
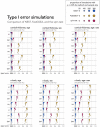
Functional networks often guide our interpretation of spatial maps of brain-phenotype associations. However, methods for assessing enrichment of associations within networks of interest have varied in terms of both scientific rigor and underlying assumptions. While some approaches have relied on subjective interpretations, others have made unrealistic assumptions about spatial properties of imaging data, leading to inflated false positive rates. We seek to address this gap in existing methodology by borrowing insight from a method widely used in genetics research for testing enrichment of associations between a set of genes and a phenotype of interest. We propose network enrichment significance testing (NEST), a flexible framework for testing the specificity of brain-phenotype associations to functional networks or other sub-regions of the brain. We apply NEST to study enrichment of associations with structural and functional brain imaging data from a large-scale neurodevelopmental cohort study.
Keywords: brain networks; brain‐phenotype associations; enrichment; hypothesis testing.
© 2024 The Author(s). Human Brain Mapping published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Russell T. Shinohara receives consulting income from Octave Bioscience and compensation for reviewership duties from the American Medical Association. Aaron Alexander‐Bloch receives consulting income from Octave Bioscience and holds equity and serves on the board of directors of Centile Biosciences. Mingyao Li receives research funding from Biogen Inc. that is unrelated to the current manuscript.
Figures



Update of
-
Network Enrichment Significance Testing in Brain-Phenotype Association Studies.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 13:2023.11.10.566593. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.10.566593. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Hum Brain Mapp. 2024 Jun 1;45(8):e26714. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26714. PMID: 38014137 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Baller, E. B. , Valcarcel, A. M. , Adebimpe, A. , Alexander‐Bloch, A. , Cui, Z. , Gur, R. C. , Gur, R. E. , Larsen, B. L. , Linn, K. A. , O'Donnell, C. M. , Pines, A. R. , Raznahan, A. , Roalf, D. R. , Sydnor, V. J. , Tapera, T. M. , Tisdall, M. D. , Vandekar, S. , Xia, C. H. , Detre, J. A. , … Satterthwaite, T. D. (2022). Developmental coupling of cerebral blood flow and fMRI fluctuations in youth. Cell Reports, 38(13), 110576. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baum, G. L. , Cui, Z. , Roalf, D. R. , Ciric, R. , Betzel, R. F. , Larsen, B. , Cieslak, M. , Cook, P. A. , Xia, C. H. , Moore, T. M. , Ruparel, K. , Oathes, D. J. , Alexander‐Bloch, A. F. , Shinohara, R. T. , Raznahan, A. , Gur, R. E. , Gur, R. C. , Bassett, D. S. , & Satterthwaite, T. D. (2019). Development of structure–function coupling in human brain networks during youth. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117(1), 771–778. 10.1073/pnas.1912034117 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belzunce, F. , Riquelme, C. M. , & Mulero, J. (2015). An introduction to stochastic orders. Academic Press.
-
- Burt, J. B. , Helmer, M. , Shinn, M. , Anticevic, A. , & Murray, J. D. (2020). Generative modeling of brain maps with spatial autocorrelation. NeuroImage, 220, 117038. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R37 MH125829/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23MH113118/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH120482/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH133118/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH112847/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH113550/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01EB022573/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH119219/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH123563/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- Brain and Behavior Research Foundation
- 1ZIAMH002949/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH132934/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH112847/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB022573/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS112274/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH123550/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH123563/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- L30 MH127652/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS112274/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH120482/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH132934/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH113550/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA MH002949/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R37MH125829/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH123550/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH119219/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

