Modulation of anti-cardiac fibrosis immune responses by changing M2 macrophages into M1 macrophages
- PMID: 38879491
- PMCID: PMC11179216
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-024-00858-z
Modulation of anti-cardiac fibrosis immune responses by changing M2 macrophages into M1 macrophages
Abstract
Background: Macrophages play a crucial role in the development of cardiac fibrosis (CF). Although our previous studies have shown that glycogen metabolism plays an important role in macrophage inflammatory phenotype, the role and mechanism of modifying macrophage phenotype by regulating glycogen metabolism and thereby improving CF have not been reported.
Methods: Here, we took glycogen synthetase kinase 3β (GSK3β) as the target and used its inhibitor NaW to enhance macrophage glycogen metabolism, transform M2 phenotype into anti-fibrotic M1 phenotype, inhibit fibroblast activation into myofibroblasts, and ultimately achieve the purpose of CF treatment.
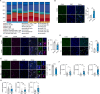
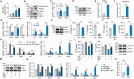
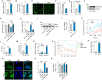
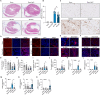
Results: NaW increases the pH of macrophage lysosome through transmembrane protein 175 (TMEM175) and caused the release of Ca2+ through the lysosomal Ca2+ channel mucolipin-2 (Mcoln2). At the same time, the released Ca2+ activates TFEB, which promotes glucose uptake by M2 and further enhances glycogen metabolism. NaW transforms the M2 phenotype into the anti-fibrotic M1 phenotype, inhibits fibroblasts from activating myofibroblasts, and ultimately achieves the purpose of treating CF.
Conclusion: Our data indicate the possibility of modifying macrophage phenotype by regulating macrophage glycogen metabolism, suggesting a potential macrophage-based immunotherapy against CF.
Keywords: Cardiac fibrosis; Glycogen; Macrophage; TMEM175.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition attenuates fibroblast activation and development of fibrosis following renal ischemia-reperfusion in mice.Dis Model Mech. 2015 Aug 1;8(8):931-40. doi: 10.1242/dmm.020511. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Dis Model Mech. 2015. PMID: 26092126 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing the Role of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3α/β in Macrophage Polarization and the Regulation of Pro-Atherogenic Pathways in Cultured Ldlr-/- Macrophages.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 30;12:676752. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.676752. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34394077 Free PMC article.
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 reduces cardiac fibrosis and promotes M2 macrophage polarization in inflammatory cardiomyopathy.Basic Res Cardiol. 2021 Jan 11;116(1):1. doi: 10.1007/s00395-020-00840-w. Basic Res Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33432417 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac macrophages adopt profibrotic/M2 phenotype in infarcted hearts: Role of urokinase plasminogen activator.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017 Jul;108:42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.05.016. Epub 2016 Jun 1. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 27262672
-
Macrophages and cadherins in fibrosis and systemic sclerosis.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2019 Nov;31(6):582-588. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000657. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 31436586 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone Deacetylase 6 Controls Atrial Fibrosis and Remodeling in Postinfarction Mice Through the Modulation of Wnt3a/GSK-3β Signaling.FASEB J. 2025 May 31;39(10):e70650. doi: 10.1096/fj.202500371R. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 40377174 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages in organ fibrosis: from pathogenesis to therapeutic targets.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Dec 4;10(1):487. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02247-1. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39632841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the Roles of Macrophages in Vascularized Composite Allotransplantation.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 10;13(6):1425. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061425. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex regulation of cardiac fibrosis: insights from immune cells and signaling pathways.J Transl Med. 2025 Feb 28;23(1):242. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06260-5. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40022104 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

