Medial cortical bone thickness of the tibial diaphysis in osteoarthritis is related to lower extremity alignment and tibial morphology
- PMID: 38879553
- PMCID: PMC11179327
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-024-04849-y
Medial cortical bone thickness of the tibial diaphysis in osteoarthritis is related to lower extremity alignment and tibial morphology
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to clarify (1) the differences in cortical bone thickness (CBT) of the tibial diaphysis between healthy and osteoarthritic knees and (2) the influences of the femorotibial angle (FTA) and inclination of the medial compartment of the proximal tibia (MCT) on tibial CBT.
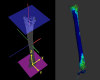
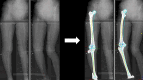
Methods: The study assessed 60 subjects with varus knee osteoarthritis (OA) (22 males and 38 females; mean age, 74 ± 7 years) and 53 healthy elderly subjects (28 males and 25 females; mean age, 70 ± 6 years). Three-dimensional estimated CBT of the tibial diaphysis was automatically calculated for 2752-11,296 points using high-resolution measurements from CT. The standardized CBT was assessed in 24 regions by combining six heights and four areas. Additionally, the association between the CBT, each FTA, and MCT inclination was investigated.
Results: The OA group showed a thicker CBT in the medial areas than in the lateral areas of the proximal tibia, while the healthy group had a thicker lateral CBT. The medial-to-lateral ratio of the proximal tibia was significantly higher in the OA group than in the healthy group. The proximal-medial CBT correlated with FTA and MCT inclinations in the OA group.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that varus osteoarthritic knees showed a different trend of proximal-medial CBT with associations in FTA and MCT inclination from healthy knees, possibly due to medial load concentration.
Keywords: Alignment; Cortical bone thickness; Healthy; Inclination of the medial compartment of the proximal tibia; Knee osteoarthritis; Tibia.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
External torsion in a proximal tibia and internal torsion in a distal tibia occur independently in varus osteoarthritic knees compared to healthy knees.J Orthop Sci. 2017 May;22(3):501-505. doi: 10.1016/j.jos.2017.01.002. Epub 2017 Jan 27. J Orthop Sci. 2017. PMID: 28139346
-
The medial inclination of the proximal tibia is associated with the external knee adduction moment in advanced varus knee osteoarthritis.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022 Feb;30(2):574-583. doi: 10.1007/s00167-020-06323-8. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022. PMID: 33067660
-
Varus inclination of the tibia is related to patellofemoral osteoarthritis in Japanese female patients with moderate knee osteoarthritis.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021 Feb;29(2):652-658. doi: 10.1007/s00167-020-06000-w. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021. PMID: 32318752
-
Articular surface of the medial proximal tibia is aligned parallel to the ground in three-dimensional space under weight-bearing conditions in healthy and varus osteoarthritic knees.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020 Oct;28(10):3232-3239. doi: 10.1007/s00167-019-05829-0. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020. PMID: 31853619
-
The varus alignment and morphologic alterations of proximal tibia affect the onset of medial knee osteoarthritis in rural Japanese women: Case control study from the longitudinal evaluation of Matsudai Knee Osteoarthritis Survey.J Orthop Sci. 2016 Mar;21(2):166-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jos.2015.12.002. Epub 2016 Jan 14. J Orthop Sci. 2016. PMID: 26778626
References
-
- Higano Y, Hayami T, Omori G, Koga Y, Endo K, Endo N. The varus alignment and morphologic alterations of proximal tibia affect the onset of medial knee osteoarthritis in rural Japanese women: case control study from the longitudinal evaluation of Matsudai knee Osteoarthritis Survey. J Orthop Sci. 2016;21:166–71. doi: 10.1016/j.jos.2015.12.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maeda K, Mochizuki T, Kobayashi K, Tanifuji O, Someya K, Hokari S, Katsumi R, Morise Y, Koga H, Sakamoto M, Koga Y, Kawashima H. Cortical thickness of the tibial diaphysis reveals age- and sex-related characteristics between non-obese healthy young and elderly subjects depending on the tibial regions. J Exp Orthop. 2020;7(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s40634-020-00297-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Someya K, Mochizuki T, Hokari S, Tanifuji O, Katsumi R, Koga H, Takahashi Y, Kobayashi K, Morise Y, Sakamoto M, Koga Y, Endo N. Age- and sex-related characteristics in cortical thickness of femoral diaphysis for young and elderly subjects. J Bone Min Metab. 2020;38:533–43. doi: 10.1007/s00774-019-01079-9. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

