Baricitinib ameliorates inflammatory and neuropathic pain in collagen antibody-induced arthritis mice by modulating the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 pathway and CSF-1 expression in dorsal root ganglion neurons
- PMID: 38879555
- PMCID: PMC11179219
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-024-03354-1
Baricitinib ameliorates inflammatory and neuropathic pain in collagen antibody-induced arthritis mice by modulating the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 pathway and CSF-1 expression in dorsal root ganglion neurons
Abstract
Background: Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, such as baricitinib, are widely used to treat rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Clinical studies show that baricitinib is more effective at reducing pain than other similar drugs. Here, we aimed to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying the pain relief conferred by baricitinib, using a mouse model of arthritis.
Methods: We treated collagen antibody-induced arthritis (CAIA) model mice with baricitinib, celecoxib, or vehicle, and evaluated the severity of arthritis, histological findings of the spinal cord, and pain-related behaviours. We also conducted RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) to identify alterations in gene expression in the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) following baricitinib treatment. Finally, we conducted in vitro experiments to investigate the direct effects of baricitinib on neuronal cells.
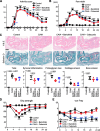
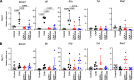
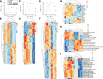
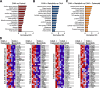
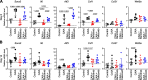
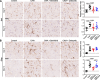
Results: Both baricitinib and celecoxib significantly decreased CAIA and improved arthritis-dependent grip-strength deficit, while only baricitinib notably suppressed residual tactile allodynia as determined by the von Frey test. CAIA induction of inflammatory cytokines in ankle synovium, including interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6, was suppressed by treatment with either baricitinib or celecoxib. In contrast, RNA-seq analysis of the DRG revealed that baricitinib, but not celecoxib, restored gene expression alterations induced by CAIA to the control condition. Among many pathways changed by CAIA and baricitinib treatment, the interferon-alpha/gamma, JAK-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathways were considerably decreased in the baricitinib group compared with the celecoxib group. Notably, only baricitinib decreased the expression of colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF-1), a potent cytokine that causes neuropathic pain through activation of the microglia-astrocyte axis in the spinal cord. Accordingly, baricitinib prevented increases in microglia and astrocytes caused by CAIA. Baricitinib also suppressed JAK/STAT3 pathway activity and Csf1 expression in cultured neuronal cells.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate the effects baricitinib has on the DRG in relation to ameliorating both inflammatory and neuropathic pain.
Keywords: Baricitinib; CAIA model; JAK/STAT3 pathway; Pain-related behaviour; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
This work was partially supported by Eli Lilly Japan K.K. NI and MT are employees of Eli Lilly Japan K.K. and a minor shareholders of Eli Lilly and Company. The authors declare no other potential competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

