The Global Historical Climatology Network Monthly Precipitation Dataset, Version 4
- PMID: 38879587
- PMCID: PMC11180175
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-024-03457-z
The Global Historical Climatology Network Monthly Precipitation Dataset, Version 4
Abstract
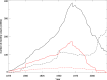
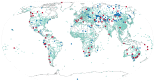
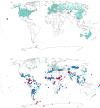
The Global Historical Climatology Network (GHCN) monthly precipitation dataset contains historical time series for thousands of land surface stations worldwide. Initially released in 1992 and revised in 1998, the dataset has been employed in a variety of applications over the past three decades, including operational monitoring, applied research, and international assessments. This paper describes the data and methods used to compile the latest edition (version 4), which has three major enhancements. The first enhancement is to the station network, which increased in size by a factor of five due to the inclusion of dozens of new source datasets, most notably GHCN Daily (GHCNd). The second improvement is the application of a rule-based algorithm to compare and merge records representing the same location. The third enhancement is to the quality assurance approach, now consisting of 18 new checks based on GHCNd and other operational systems. Updated monthly, the resulting dataset consists of time series of monthly precipitation totals at more than 120,000 worldwide stations, including more than 33,000 active observing sites.
© 2024. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Newly reconstructed Arctic surface air temperatures for 1979-2021 with deep learning method.Sci Data. 2023 Mar 15;10(1):140. doi: 10.1038/s41597-023-02059-5. Sci Data. 2023. PMID: 36922501 Free PMC article.
-
HYADES - A Global Archive of Annual Maxima Daily Precipitation.Sci Data. 2024 Mar 15;11(1):298. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03109-2. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 38491034 Free PMC article.
-
Very high resolution, altitude-corrected, TMPA-based monthly satellite precipitation product over the CONUS.Sci Data. 2020 Mar 3;7(1):74. doi: 10.1038/s41597-020-0411-0. Sci Data. 2020. PMID: 32127530 Free PMC article.
-
1 km monthly precipitation and temperatures dataset for China from 1952 to 2019 based on new baseline climatology surfaces.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Jan 1;906:167613. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167613. Epub 2023 Oct 7. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 37813268
-
Dataset of gridded time series of monthly air temperature (min, max, mean) and atmospheric precipitation for Ukraine covering the period of 1946-2020.Data Brief. 2022 Aug 24;44:108553. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2022.108553. eCollection 2022 Oct. Data Brief. 2022. PMID: 36111286 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The global historical climate database HCLIM.Sci Data. 2023 Jan 19;10(1):44. doi: 10.1038/s41597-022-01919-w. Sci Data. 2023. PMID: 36658229 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term homogenized air temperature and precipitation datasets in Romania, 1901-2023.Sci Data. 2025 Jul 1;12(1):1116. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-05371-4. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 40595673 Free PMC article.
-
SC-PREC4SA: A serially complete daily precipitation dataset for South America.Sci Data. 2025 Jun 14;12(1):1006. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-05312-1. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 40517157 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vose, R. S. et al. The Global Historical Climatology Network: Long-term monthly temperature, precipitation, sea level pressure, and station pressure data. 324 (Oak Ridge National Laboratory Environmental Sciences Division, 1992).
-
- Vose, R. S., Peterson, T. C. & Hulme, M. The Global Historical Climatology Network precipitation data set: Version 2.0. Ninth Symposium on Global Change Studies, 103-104 (1998).
-
- Gulev, S. K. et al. Changing state of the climate system. Climate change, 287-422 (2021).
-
- Funk C, et al. A global satellite-assisted precipitation climatology. Earth System Science Data. 2015;7:275–287. doi: 10.5194/essd-7-275-2015. - DOI
-
- Schneider, U., Finger, P., Rustemeier, E., Ziese, M. & Hänsel, S. Global Precipitation Analysis Products of the GPCC. (Deutscher Wetterdienst, 2022).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

