The comparison of white-to-white via triple person-times caliper measuring and machine-measuring in V4c implantable collamer lens implantation
- PMID: 38880805
- PMCID: PMC11180651
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-64647-8
The comparison of white-to-white via triple person-times caliper measuring and machine-measuring in V4c implantable collamer lens implantation
Abstract
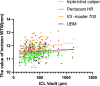
This study aimed to compare the differences and characteristics of white-to-white (WTW) values obtained before V4c implantation using triple person-times caliper, IOL-Master 700, Pentacam HR, and UBM, and to assess their correlation with vaulting. A total of 930 myopia patients (1842 eyes) who were interested in undergoing ICL surgery were assessed before the procedure using various instruments. The WTW measurements were obtained using a triple person-times caliper, Pentacam HR, and IOL-Master 700, whereas the angle-to-angle (ATA) measurements were obtained using UBM. The size of the ICL was subsequently calculated using triple person-times caliper measurements. The vault of the ICL was assessed using Pentacam HR three months after the surgery. The WTW was determined to be 11.30 ± 0.29 mm, 11.43 ± 0.29 mm, and11.86 ± 0.38 mm, respectively, using the triple person-times caliper, Pentacam HR, and IOL-Master 700. The measurement of ATA was 11.57 ± 0.51 mm, as done by UBM. The ICL vault was measured to be 400.97 ± 198.46 µm when examined with Pentacam HR three monthsafter the procedure. The linear regression analyses of ICL size and WTW of triple person-times caliper, ICL vault and WTW were (R = 0.703, p < 0.001; R = 0.0969, p < 0.001) respectively. The highest correlation was found between IOL-Master and Pentacam HR (r = 0.766, p = 0.000). The lowest correlation was found between UBM and Pentacam HR (r = 0.358, p = 0.002). Bland-Altman analysis showed that the 95% limits of agreement (LoA) were the triple person-times caliper and Pentacam HR (- 0.573, 0.298) and the triple person-times caliper and UBM (- 1.15, - 0.605). This indicated a strong agreement between the triple person-times caliper and Pentacam HR and a lack of agreement between the triple person-times caliper and UBM. Triple person-times caliper measurements offer excellent maneuverability, practicality, and reliable outcomes for determining ICL vaults. Measurements obtained using the triple-person caliper were less differece than those obtained using the Pentacam HR.
Keywords: Caliper; ICL; IOL-Master; Pentacam HR; UBM; White-to-white.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparative study of anterior segment measurements using 3 different instruments in myopic patients after ICL implantation.BMC Ophthalmol. 2019 Aug 13;19(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s12886-019-1194-y. BMC Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31409385 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of early changes in and factors affecting vault following posterior chamber phakic Implantable Collamer Lens implantation without and with a central hole (ICL V4 and ICL V4c).BMC Ophthalmol. 2016 Sep 7;16(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s12886-016-0336-8. BMC Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 27604229 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of white-to-white measurements using four devices and their determination of ICL sizing.Eye Vis (Lond). 2022 Oct 2;9(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40662-022-00308-z. Eye Vis (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36182955 Free PMC article.
-
Implantable Collamer Lens Procedure Planning: A Review of Global Approaches.Clin Ophthalmol. 2024 Apr 6;18:1033-1043. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S456397. eCollection 2024. Clin Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38601168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Posterior-chamber phakic implantable collamer lenses with a central port: a review.Acta Ophthalmol. 2021 May;99(3):e288-e301. doi: 10.1111/aos.14599. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Acta Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 32841517 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

