Identification and verification of circRNA biomarkers for coronary artery disease based on WGCNA and the LASSO algorithm
- PMID: 38880872
- PMCID: PMC11181640
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-024-03972-2
Identification and verification of circRNA biomarkers for coronary artery disease based on WGCNA and the LASSO algorithm
Abstract
Background: The role of circular RNAs (circRNAs) as biomarkers of coronary artery disease (CAD) remains poorly explored. This study aimed to identify and validate potential circulating circRNAs as biomarkers for the diagnosis of CAD.
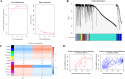
Methods: The expression profile of circRNAs associated with CAD was obtained from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Differential expression analysis, weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) and least absolute shrinkage and selection operation (LASSO) were employed to identify CAD-related hub circRNAs. The expression levels of these hub circRNAs were validated using qRT-PCR in blood samples from 100 CAD patients and 100 controls. The diagnostic performance of these circRNAs was evaluated through logistic regression analysis, receiver operator characteristic (ROC) analysis, integrated discrimination improvement (IDI), and net reclassification improvement (NRI). Functional enrichment analyses were performed to predict the possible mechanisms of circRNAs in CAD.
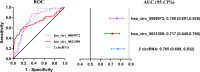
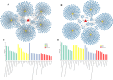
Results: A total of ten CAD-related hub circRNAs were identified through WGCNA and LASSO analysis. Among them, hsa_circ_0069972 and hsa_circ_0021509 were highly expressed in blood samples of CAD patients, and they were identified as independent predictors after adjustment for relevant confounders. The area under the ROC curve for hsa_circ_0069972 and hsa_circ_0021509 was 0.760 and 0.717, respectively. The classification of patients was improved with the incorporation of circRNAs into the clinical model composed of conventional cardiovascular risk factors, showing an IDI of 0.131 and NRI of 0.170 for hsa_circ_0069972, and an IDI of 0.111 and NRI of 0.150 for hsa_circ_0021509. Functional enrichment analyses revealed that the hsa_circ_0069972-miRNA-mRNA network was enriched in TGF-β、FoxO and Hippo signaling pathways, while the hsa_circ_0021509-miRNA-mRNA network was enriched in PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways.
Conclusion: Hsa_circ_0069972 and hsa_circ_0021509 were identified by integrated analysis, and they are highly expressed in CAD patients. They may serve as novel biomarkers for CAD.
Keywords: Biomarker; Circular RNA; Coronary artery disease; LASSO; WGCNA.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Plasma circular RNA hsa_circ_0001445 and coronary artery disease: Performance as a biomarker.FASEB J. 2020 Mar;34(3):4403-4414. doi: 10.1096/fj.201902507R. Epub 2020 Jan 30. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 31999007
-
A novel circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network identifies circ-YOD1 as a biomarker for coronary artery disease.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 4;9(1):18314. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54603-2. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31797949 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of circular RNA Hsa_circ_0001879 and Hsa_circ_0004104 as novel biomarkers for coronary artery disease.Atherosclerosis. 2019 Jul;286:88-96. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.05.006. Epub 2019 May 9. Atherosclerosis. 2019. PMID: 31103880
-
A two-circular RNA signature as a noninvasive diagnostic biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma.J Transl Med. 2019 Feb 18;17(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-1800-z. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 30777071 Free PMC article.
-
A review of cutting-edge biomarkers for diagnosing coronary artery disease.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jan 24;104(4):e41377. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041377. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 39854741 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circular RNAs in coronary heart disease: From molecular mechanism to promising clinical application (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Jan;55(1):11. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5452. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39513584 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Holm NR, Makikallio T, Lindsay MM, Spence MS, Erglis A, Menown IBA, et al. Percutaneous coronary angioplasty versus coronary artery bypass grafting in the treatment of unprotected left main stenosis: updated 5-year outcomes from the randomised, non-inferiority NOBLE trial. Lancet. 2020;395(10219):191–9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32972-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 202303/Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Pathophysiology
- 202303/Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Pathophysiology
- 202303/Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Pathophysiology
- 2023C04017/Key R & D Program of Zhejiang
- 2023C04017/Key R & D Program of Zhejiang
- 2023C04017/Key R & D Program of Zhejiang
- 2023-144/Natural Science Foundation of Ningbo Municipality
- 2023-144/Natural Science Foundation of Ningbo Municipality
- 2023-144/Natural Science Foundation of Ningbo Municipality
- ZX2023000225/Science and technology cooperation project of "Vanguard" "Leading goose" of Zhejiang Province
- ZX2023000225/Science and technology cooperation project of "Vanguard" "Leading goose" of Zhejiang Province
- ZX2023000225/Science and technology cooperation project of "Vanguard" "Leading goose" of Zhejiang Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

