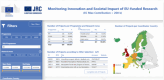
Return on investment in science: twenty years of European Commission funded research in Alzheimer's dementia, breast cancer and prostate cancer
- PMID: 38880873
- PMCID: PMC11181594
- DOI: 10.1186/s12962-024-00540-5
Return on investment in science: twenty years of European Commission funded research in Alzheimer's dementia, breast cancer and prostate cancer
Abstract
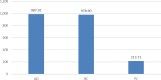
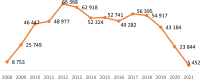
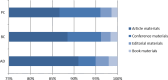
Alzheimer's disease (AD), breast cancer (BC) and prostate cancer (PC) continue to be high in the research and innovation agenda of the European Commission (EC). This is due to their exceptionally large burden to the national health systems, the profound economic effects of opportunity costs attributable to decreased working ability, premature mortality and the ever-increasing demand for both hospital and home-based medical care. Over the last two decades, the EC has been steadily increasing both the number of proposals being funded and the amounts of financial resources being allocated to these fields of research. This trend has continued throughout four consecutive science funding cycles, namely framework programme (FP)5, FP6, FP7 and Horizon 2020 (H2020). We performed a retrospective assessment of the outputs and outcomes of EC funding in AD, BC and PC research over the 1999-2019 period by means of selected indicators. These indicators were assessed for their ability to screen the past, present and future for an array of causal relationships and long-term trends in clinical, epidemiological and public health sphere, while considering also the broader socioeconomic impact of funded research on the society at large. This analysis shows that public-private partnerships with large industry and university-based consortia have led to some of the most impactful proposals being funded over the analysed time period. New pharmaceuticals, small molecules and monoclonal antibodies alike, along with screening and prevention, have been the most prominent sources of innovation in BC and PC, extending patients' survival and enhancing their quality of life. Unlike oncology, dementia drug development has been way less successful, with only minor improvements related to the quality of supportive medical care for symptoms and more sensitive diagnostics, without any ground-breaking disease-modifying treatment(s). Significant progresses in imaging diagnostics and nanotechnology have been largely driven by the participation of medical device industry multinational companies. Clinical trials funded by the EC were conducted, leading to the development of brand-new drug molecules featuring novel mechanisms of action. Some prominent cases of breakthrough discoveries serve as evidence for the European capability to generate cutting-edge technological innovation in biomedicine. Less productive areas of research may be reconsidered as priorities when shaping the new agenda for forthcoming science funding programmes.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Breast cancer; European Commission; FP5; FP6; FP7; Funding; Horizon 2020; Indicators; Innovation; Investment; Medical care; Outcomes; Pharmaceuticals; Policy; Prostate cancer; Public P&R funding; Public investment; Research policy; Return on investment (RoI).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exploring the connection between EU-funded research and methodological approaches: insights from a retrospective analysis.J Transl Med. 2024 Oct 3;22(1):891. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05557-1. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39363357 Free PMC article.
-
Gauging innovation and health impact from biomedical research: survey results and interviews with recipients of EU-funding in the fields of Alzheimer's disease, breast cancer and prostate cancer.Health Res Policy Syst. 2023 Jun 29;21(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12961-023-00981-z. Health Res Policy Syst. 2023. PMID: 37386455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EU FP7 research funding for an orphan drug (Orfadin®) and vaccine (Hep C) development: a success and a failure?J Pharm Policy Pract. 2021 Apr 28;14(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s40545-021-00317-8. J Pharm Policy Pract. 2021. PMID: 33910624 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's Disease, and Breast and Prostate Cancer Research: Translational Failures and the Importance to Monitor Outputs and Impact of Funded Research.Animals (Basel). 2020 Jul 14;10(7):1194. doi: 10.3390/ani10071194. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32674379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Minderoo-Monaco Commission on Plastics and Human Health.Ann Glob Health. 2023 Mar 21;89(1):23. doi: 10.5334/aogh.4056. eCollection 2023. Ann Glob Health. 2023. PMID: 36969097 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Global, regional, and national burden of genitourinary cancers in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2021.J Natl Cancer Cent. 2025 May 3;5(3):330-345. doi: 10.1016/j.jncc.2025.03.001. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Natl Cancer Cent. 2025. PMID: 40693231 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the connection between EU-funded research and methodological approaches: insights from a retrospective analysis.J Transl Med. 2024 Oct 3;22(1):891. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05557-1. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39363357 Free PMC article.
References
-
- https://nap.nationalacademies.org/read/10030/chapter/3#16. Accessed 1 Aug 2023.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

