Using neural biomarkers to personalize dosing of vagus nerve stimulation
- PMID: 38880906
- PMCID: PMC11181600
- DOI: 10.1186/s42234-024-00147-4
Using neural biomarkers to personalize dosing of vagus nerve stimulation
Abstract
Background: Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is an established therapy for treating a variety of chronic diseases, such as epilepsy, depression, obesity, and for stroke rehabilitation. However, lack of precision and side-effects have hindered its efficacy and extension to new conditions. Achieving a better understanding of the relationship between VNS parameters and neural and physiological responses is therefore necessary to enable the design of personalized dosing procedures and improve precision and efficacy of VNS therapies.
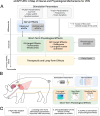
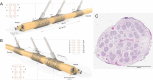
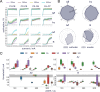
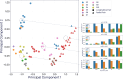
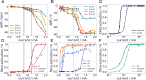
Methods: We used biomarkers from recorded evoked fiber activity and short-term physiological responses (throat muscle, cardiac and respiratory activity) to understand the response to a wide range of VNS parameters in anaesthetised pigs. Using signal processing, Gaussian processes (GP) and parametric regression models we analyse the relationship between VNS parameters and neural and physiological responses.
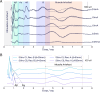
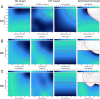
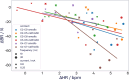
Results: Firstly, we illustrate how considering multiple stimulation parameters in VNS dosing can improve the efficacy and precision of VNS therapies. Secondly, we describe the relationship between different VNS parameters and the evoked fiber activity and show how spatially selective electrodes can be used to improve fiber recruitment. Thirdly, we provide a detailed exploration of the relationship between the activations of neural fiber types and different physiological effects. Finally, based on these results, we discuss how recordings of evoked fiber activity can help design VNS dosing procedures that optimize short-term physiological effects safely and efficiently.
Conclusion: Understanding of evoked fiber activity during VNS provide powerful biomarkers that could improve the precision, safety and efficacy of VNS therapies.
Keywords: Biomarker; Heart failure; Neuromodulation; Vagus nerve stimulation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors, except AT, are (or were at the time of their contribution) employees of BIOS Health Ltd., and declare that BIOS Health has filed US and international patent applications relating to a system, apparatus and method for utilising neural biomarker response in clinical decision-making. The concepts of this work is contained in the UK Patent GB 2214547.8. AT declares a consulting role with BIOS Health at the time the research was conducted. GL holds a position at the Université de Montréal and Mila-Quebec AI Institute and declares receiving funding from BIOS Health Ltd topics related to the present publication, but that was not in place at the time of the development of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Aristovich K, Donega M, Fjordbakk C, Tarotin I, Chapman C, Viscasillas J, et al. Model-based geometrical optimisation and in vivo validation of a spatially selective multielectrode cuff array for vagus nerve neuromodulation. arXiv:1903.12459 [physics]. 2020. ArXiv: 1903.12459. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
