Rewiring the Sex-Determination Pathway During the Evolution of Self-Fertility
- PMID: 38880992
- PMCID: PMC11180601
- DOI: 10.1093/molbev/msae101
Rewiring the Sex-Determination Pathway During the Evolution of Self-Fertility
Abstract
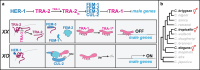
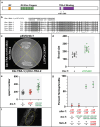
Although evolution is driven by changes in how regulatory pathways control development, we know little about the molecular details underlying these transitions. The TRA-2 domain that mediates contact with TRA-1 is conserved in Caenorhabditis. By comparing the interaction of these proteins in two species, we identified a striking change in how sexual development is controlled. Identical mutations in this domain promote oogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans but promote spermatogenesis in Caenorhabditis briggsae. Furthermore, the effects of these mutations involve the male-promoting gene fem-3 in C. elegans but are independent of fem-3 in C. briggsae. Finally, reciprocal mutations in these genes show that C. briggsae TRA-2 binds TRA-1 to prevent expression of spermatogenesis regulators. By contrast, in C. elegans TRA-1 sequesters TRA-2 in the germ line, allowing FEM-3 to initiate spermatogenesis. Thus, we propose that the flow of information within the sex determination pathway has switched directions during evolution. This result has important implications for how evolutionary change can occur.
Keywords: evolution of gene regulation; nematodes; sex determination.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution 2024.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

