Accelerating human-computer interaction through convergent conditions for LLM explanation
- PMID: 38881954
- PMCID: PMC11177345
- DOI: 10.3389/frai.2024.1406773
Accelerating human-computer interaction through convergent conditions for LLM explanation
Abstract
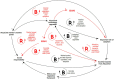
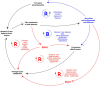
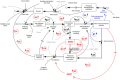
The article addresses the accelerating human-machine interaction using the large language model (LLM). It goes beyond the traditional logical paradigms of explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) by considering poor-formalizable cognitive semantical interpretations of LLM. XAI is immersed in a hybrid space, where humans and machines have crucial distinctions during the digitisation of the interaction process. The author's convergent methodology ensures the conditions for making XAI purposeful and sustainable. This methodology is based on the inverse problem-solving method, cognitive modeling, genetic algorithm, neural network, causal loop dynamics, and eigenform realization. It has been shown that decision-makers need to create unique structural conditions for information processes, using LLM to accelerate the convergence of collective problem solving. The implementations have been carried out during the collective strategic planning in situational centers. The study is helpful for the advancement of explainable LLM in many branches of economy, science and technology.
Keywords: LLM; causal loop dynamics; cognitive semantics; cybernetics; eigenforms; explainable artificial intelligence; hybrid reality; socio-economic environment.
Copyright © 2024 Raikov, Giretti, Pirani, Spalazzi and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Adadi A., Berrada M. (2018). Peeking inside the black-box: a survey on explainable artificial intelligence (XAI). IEEE Access. 6, 52138–52160. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2870052 - DOI
-
- Albantakis L., Tononi G. (2021). What we are is more than what we do. arXiv [Epubh ahead of print]. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2102.04219 - DOI
-
- Albarracin M., Hipólito I., Tremblay S. E., Fox J. G., René G., Friston K., et al. . (2023). “Designing explainable artificial intelligence with active inference: a framework for transparent introspection and decision-making” in Active inference. IWAI 2023. Communications in Computer and Information Science, 1915. eds. Buckley C. L., Cialfi D., Lanillos P., Ramstead M., Sajid N., Shimazaki H., et al.. (Cham: Springer; ).
-
- Arrieta A. B., Díaz-Rodríguez N., Del Ser J., Bennetot A., Tabik S., Barbado A., et al. . (2020). Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI): concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges towards responsible AI. Inf. Fusion 58, 82–115. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2019.12.012 - DOI
-
- Bangu S. (2017). Scientific explanation and understanding: unificationism reconsidered. Eur. J. Philos. Sci. 7, 103–126. doi: 10.1007/s13194-016-0148-y - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

