Host Factors Modulate Virus-Induced IFN Production via Pattern Recognition Receptors
- PMID: 38882189
- PMCID: PMC11180453
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S455035
Host Factors Modulate Virus-Induced IFN Production via Pattern Recognition Receptors
Abstract
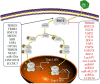
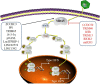
Innate immunity is the first line of defense in the human body, and it plays an important role in defending against viral infection. Viruses are identified by different pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) that activate the mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein (MAVS) or transmembrane protein 173 (STING), which trigger multiple signaling cascades that cause nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) to produce inflammatory factors and interferons (IFNs). PRRs play a pivotal role as the first step in pathogen induction of interferon production. Interferon elicits antiviral activity by inducing the transcription of hundreds of IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) via the janus kinase (JAK) - signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway. An increasing number of studies have shown that environmental, pathogen and host factors regulate the IFN signaling pathway. Here, we summarize the mechanisms of host factor modulation in IFN production via pattern recognition receptors. These regulatory mechanisms maintain interferon levels in a normal state and clear viruses without inducing autoimmune disease.
Keywords: host factors; interferon-signaling pathway; pattern recognition receptors.
© 2024 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
RIG-I is a key antiviral interferon-stimulated gene against hepatitis E virus regardless of interferon production.Hepatology. 2017 Jun;65(6):1823-1839. doi: 10.1002/hep.29105. Epub 2017 May 3. Hepatology. 2017. PMID: 28195391
-
Web of interferon stimulated antiviral factors to control the influenza A viruses replication.Microb Pathog. 2020 Feb;139:103919. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103919. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Microb Pathog. 2020. PMID: 31830579 Review.
-
Human IFIT3 Protein Induces Interferon Signaling and Inhibits Adenovirus Immediate Early Gene Expression.mBio. 2021 Dec 21;12(6):e0282921. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02829-21. Epub 2021 Nov 2. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34724821 Free PMC article.
-
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Protein Suppresses Type I and Type III Interferon Induction by Targeting RIG-I Signaling.J Virol. 2020 Jun 16;94(13):e00099-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00099-20. Print 2020 Jun 16. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32295922 Free PMC article.
-
Interferons: Tug of War Between Bacteria and Their Host.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Mar 10;11:624094. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.624094. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33777837 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of host factors for livestock and poultry viruses: genome-wide screening technology based on the CRISPR system.Front Microbiol. 2024 Nov 21;15:1498641. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1498641. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39640855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NF-κB signaling directs a program of transient amplifications at innate immune response genes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 13:2025.03.11.641929. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.11.641929. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40161744 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

