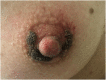
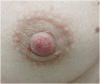
Unilateral demodicidosis of the nipple/areola complex mimicking nevoid hyperkeratosis
- PMID: 38883167
- PMCID: PMC11176602
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2024.03.024
Unilateral demodicidosis of the nipple/areola complex mimicking nevoid hyperkeratosis
Keywords: demodicidosis; demodicosis; nevoid hyperkeratosis; nipple.
Conflict of interest statement
None disclosed.
Figures


References
-
- Garven H.S. Demodex folliculorum in the human nipple. Lancet. 1946;2:44–46. - PubMed
-
- Val-Bernal J.F., Diego C., Rodriguez-Villar D., Garijo M.F. The nipple-areola complex epidermis: a prospective systematic study in adult autopsies. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:787–793. - PubMed
-
- Fidler W.J. Demodex folliculorum in a nipple imprint. Acta Cytol. 1978;22:168–169. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
