A case of damage control after polytrauma and bilateral femur fracture
- PMID: 38883269
- PMCID: PMC11176921
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcr.2024.101037
A case of damage control after polytrauma and bilateral femur fracture
Abstract
Introduction: Multi-trauma patients require a multidisciplinary team, especially in the presence of various body systems injuries. The evaluation focuses on the decision regarding the DCO and ETC approaches.
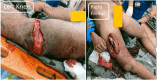
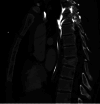
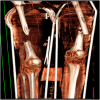
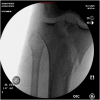
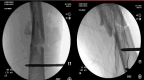
Case presentation: A 24-year-old male patient with Glasgow Coma Score 8, arrived at the emergency room, followed by ATLS protocol. Orthopedic trauma included D8 vertebra unstable burst fracture, right open femur shaft fracture, left closed midshaft femur fracture, and right tibial plateau fracture of the knee.
Case summary: A hemodynamically stable patient with bilateral femur fractures is directed toward the DCO approach.
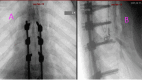
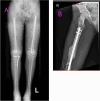
Discussion: An initial treatment for an external fixator across the knee on the right leg and a spine fusion and decompression of D5-10 surgery was made on the day of admission. Definitive fixation and conversion to internal fixators were done on day 9 after the accident. Postoperative drop-foot injury was seen in the right leg. A Masquelet technique was applied for the right femur segmental fracture due to gaps.
Conclusion: DCO may be employed to temporarily stabilize fractures, allowing the patient to recover from other life-threatening injuries before definitive fixation. Further secondary procedures, such as the Masquelet technique, should be considered to optimize the results. Long-term follow-up and rehabilitation are part of recovery, aiming to optimize functional recovery and improve the patient's quality of life.
Keywords: Damage control; Early total care; Femur shaft fracture; Masquelet; Multi trauma.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Changes in the management of femoral shaft fractures in polytrauma patients: from early total care to damage control orthopedic surgery.J Trauma. 2002 Sep;53(3):452-61; discussion 461-2. doi: 10.1097/00005373-200209000-00010. J Trauma. 2002. PMID: 12352480
-
Damage control orthopedics applied in an 8-year-old child with life-threatening multiple injuries: A CARE-compliant case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Apr;98(16):e15294. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015294. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31008978 Free PMC article.
-
Conversion of external fixation to intramedullary nailing for fractures of the shaft of the femur in multiply injured patients.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000 Jun;82(6):781-8. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000. PMID: 10859097
-
Orthopedic injuries in patients with multiple injuries: Results of the 11th trauma update international consensus conference Milan, December 11, 2017.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2020 Feb;88(2):e53-e76. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000002407. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2020. PMID: 32150031
-
Popliteal artery transection associated with a minimally displaced tibial plateau fracture: a case report and review of the literature.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020 Jan 30;21(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-3089-8. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020. PMID: 32000749 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization . World Heal Organ; 2023. Global Status Report on Road Safety 2023; p. 81.
-
- Anon. The trauma call. BMJ. 2018:361. - PubMed
-
- Cole E., Crichton N. The culture of a trauma team in relation to human factors. J. Clin. Nurs. 2006;15(10):1257–1266. - PubMed
-
- Pape H.-C., Halvachizadeh S., Leenen L., Velmahos G.D., Buckley R., Giannoudis P.V. Timing of major fracture care in polytrauma patients - an update on principles, parameters and strategies for 2020. Injury. 2019;50(10):1656–1670. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

