A cuttlefish ink nanoparticle-reinforced biopolymer hydrogel with robust adhesive and immunomodulatory features for treating oral ulcers in diabetes
- PMID: 38883310
- PMCID: PMC11179175
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.04.022
A cuttlefish ink nanoparticle-reinforced biopolymer hydrogel with robust adhesive and immunomodulatory features for treating oral ulcers in diabetes
Abstract
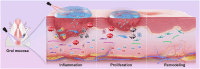
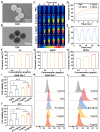
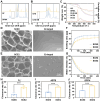
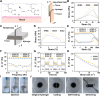
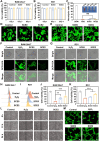
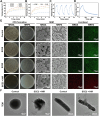
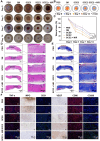
Oral ulcers can be managed using a variety of biomaterials that deliver drugs or cytokines. However, many patients experience minimal benefits from certain medical treatments because of poor compliance, short retention times in the oral cavity, and inadequate drug efficacy. Herein, we present a novel hydrogel patch (SCE2) composed of a biopolymer matrix (featuring ultraviolet-triggered adhesion properties) loaded with cuttlefish ink nanoparticles (possessing pro-healing functions). Applying a straightforward local method initiates the formation of a hydrogel barrier that adheres to mucosal injuries under the influence of ultraviolet light. SCE2 then demonstrates exceptional capabilities for near-infrared photothermal sterilization and neutralization of reactive oxygen species. These properties contribute to the elimination of bacteria and the management of the oxidation process, thus accelerating the healing phase's progression from inflammation to proliferation. In studies involving diabetic rats with oral ulcers, the SCE2 adhesive patch significantly quickens recovery by altering the inflamed state of the injured area, facilitating rapid re-epithelialization, and fostering angiogenesis. In conclusion, this light-sensitive hydrogel patch offers a promising path to expedited wound healing, potentially transforming treatment strategies for clinical oral ulcers.
Keywords: Cuttlefish ink nanoparticles; Hydrogel patches; Oral ulcers; Tissue adhesives; Wound healing.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Jianliang Shen is an editorial board member for Bioactive Materials and was not involved in the editorial review or the decision to publish this article. All authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Choi S., Jeon J., Bae Y., Hwang Y., Cho S.W. Mucoadhesive phenolic pectin hydrogels for saliva substitute and oral patch. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023;33(44)
-
- Edmans J.G., Ollington B., Colley H.E., Santocildes-Romero M.E., Siim Madsen L., Hatton P.V., Spain S.G., Murdoch C. Electrospun patch delivery of anti-TNFalpha F(ab) for the treatment of inflammatory oral mucosal disease. J. Contr. Release. 2022;350:146–157. - PubMed
-
- Mohammed E., Aboulkhair A.G., Tawifq M.M. Effect of nano-chitosan and nano-doxycycline gel on healing of induced oral ulcer in rat model: histological and immunohistochemical study. Clin. Oral Invest. 2021;26(3):3109–3118. - PubMed
-
- Wu J., Pan Z., Zhao Z.Y., Wang M.H., Dong L., Gao H.L., Liu C.Y., Zhou P., Chen L., Shi C.J., Zhang Z.Y., Yang C., Yu S.H., Zou D.H. Anti-swelling, robust, and adhesive extracellular matrix-mimicking hydrogel used as intraoral dressing. Adv. Mater. 2022;34(20) - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

