Effect of intraoperative cell salvage on coagulation function outcomes in patients with massive post-Cesarean section hemorrhage
- PMID: 38883352
- PMCID: PMC11170581
- DOI: 10.62347/UTAB1666
Effect of intraoperative cell salvage on coagulation function outcomes in patients with massive post-Cesarean section hemorrhage
Abstract
Objective: To examine the impact of using intraoperative cell salvage (ICS) for the restoration of coagulation function in cases of massive Post-Cesarean Section Hemorrhage (PCSH).
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 60 cases of massive PCSH meeting inclusion criteria at Suqian Maternity and Children's Hospital from January 2020 to July 2022. Patients were divided into two groups: allogeneic blood transfusion group (Group A, n = 30) and ICS group (Group B, n = 30), based on transfusion methods. Blood parameters, coagulation function, and adverse reactions were assessed before (T0) and after (T1) transfusion. Patients were categorized into good prognosis (GP) and poor prognosis (PP) groups based on adverse reaction occurrence. Clinical profiles were compared between groups, and multivariate binary logistic regression analysis was employed to evaluate the factors that may affect the prognosis in women with PCSH.
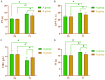
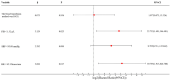
Results: No significant differences in routine blood parameters were observed between groups at T0 and T1 (P>0.05). At T0, no significant differences in PT, APTT, TT, or FIB were found between groups (P>0.05). Both groups showed a reduction in PT, APTT, and TT values at T1 compared to T0, with Group B experiencing a more significant decrease than Group A (P<0.05). FIB increased in both groups at T1 compared to T0, with Group B demonstrating a higher increase than Group A (P<0.05). Both groups showed increased blood pressure at T1 compared to T0, with Group B showing a more pronounced elevation than Group A (P<0.05). The occurrence of adverse reactions was significantly lower in Group B (1/30, 3.33%) compared to Group A (7/30, 23.33%) (P<0.05). Logistic regression analysis identified FIB<1.52 g/L and HR<45.35 times/min as factors associated with increased risk of unfavorable outcome in women with PCSH.
Conclusion: In patients experiencing significant PCSH, ICS may lead to better postoperative recovery of blood parameters, faster restoration of coagulation function, and reduced risk of adverse events compared to ABT. Moreover, early detection of coagulation function and blood gas indexes is crucial for clinicians to implement timely prevention and treatment measures.
Keywords: Intraoperative cell salvage; cesarean section; clinical outcome; coagulation function; postpartum hemorrhage.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intraoperative cell salvage is associated with reduced allogeneic blood requirements and has no significant impairment on coagulation function in patients undergoing cesarean delivery: a retrospective study.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2020 May;301(5):1173-1180. doi: 10.1007/s00404-020-05500-x. Epub 2020 Apr 4. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2020. PMID: 32248298
-
Prediction and Evaluation of Machine Learning Algorithm for Prediction of Blood Transfusion during Cesarean Section and Analysis of Risk Factors of Hypothermia during Anesthesia Recovery.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Apr 13;2022:8661324. doi: 10.1155/2022/8661324. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jun 28;2023:9863486. doi: 10.1155/2023/9863486. PMID: 35465016 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Intraoperative cell salvage as an effective intervention for postpartum hemorrhage-Evidence from a prospective randomized controlled trial.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 10;13:953334. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.953334. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36300123 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of intraoperative cell rescue on bleeding related indexes after cesarean section.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Mar 16;10(8):2439-2446. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i8.2439. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 35434071 Free PMC article.
-
[Application of goal-oriented fluid replacement therapy in volume management of postpartum hemorrhage during cesarean section].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Mar;33(3):305-310. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20201016-00672. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 33834971 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
References
-
- Franz ND, Machado-Aranda D, Miller JT, Farina N. Impact of obesity on tranexamic acid efficacy in adult patients with major bleeding. Ann Pharmacother. 2021;55:1076–1083. - PubMed
-
- Howard DC, Jones AE, Skeith A, Lai J, D’Souza R, Caughey AB. Tranexamic acid for the treatment of postpartum hemorrhage: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2022;4:100588. - PubMed
-
- Massalha M, Faranish R, Romano S, Salim R. Decreased inferior vena cava diameter as an early marker in postpartum hemorrhage. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2022;59:234–240. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
