Therapeutic and pharmacological efficacy of plant-derived bioactive compounds in targeting breast cancer
- PMID: 38883353
- PMCID: PMC11170612
- DOI: 10.62347/NUZN4999
Therapeutic and pharmacological efficacy of plant-derived bioactive compounds in targeting breast cancer
Abstract
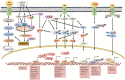
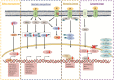
Breast cancer (BC) ranks number one among cancers affecting women globally. Serious concerns include delayed diagnosis, poor prognosis, and adverse side effects of conventional treatment, leading to residual morbidity. Therefore, an alternative treatment approach that is safe and effective has become the need of the hour. In this regard, plant-based medicines via a combination of conventional drugs are gaining increasing acceptance worldwide, playing a pivotal role in cancer management as proven by their efficacy evaluation studies. This review aims to fill the knowledge gaps by providing the preclinical evidence of cellular and molecular mechanisms of Indian phytomedicines in targeting varied pathways of breast cancer progression. A comprehensive search was performed on different platforms, followed by screening of relevant studies for review. In this article, the in-depth of various botanical drugs covering their nomenclature, dosage, toxicity, and modus operandi in BC cells have been extensively discussed. Various signaling pathways like Notch signaling, MAPK signaling, apoptosis, Wnt signaling, etc. regulated by herbal medicine treatment in BC are also highlighted to understand the drug mechanism better. This will guide the researchers to plan future strategies and generate more robust integrated evidence of plant-based drugs or botanical formulations for their potential role in the management of BC.
Keywords: Indian herbs; Phytomedicine; anticancer; breast cancer; cancer treatment; integrative oncology.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Exploration of therapeutic applicability and different signaling mechanism of various phytopharmacological agents for treatment of breast cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jul;139:111584. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111584. Epub 2021 May 10. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34243623 Review.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
The potential of natural herbal plants in the treatment and prevention of non-small cell lung cancer: An encounter between ferroptosis and mitophagy.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Apr 25;346:119555. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119555. Epub 2025 Feb 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40015539 Review.
-
A Review of Twenty Years of Research on the Regulation of Signaling Pathways by Natural Products in Breast Cancer.Molecules. 2022 May 25;27(11):3412. doi: 10.3390/molecules27113412. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35684353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the MAPK signaling pathway: implications and prospects of flavonoids in 3P medicine as modulators of cancer cell plasticity and therapeutic resistance in breast cancer patients.EPMA J. 2025 Apr 10;16(2):437-463. doi: 10.1007/s13167-025-00407-6. eCollection 2025 Jun. EPMA J. 2025. PMID: 40438489 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Daurisoline Inhibits Progression of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Regulating the γ-Secretase/Notch Axis.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2025 Mar 1;33(2):331-343. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2024.131. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2025. PMID: 39933901 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Waks AG, Winer EP. Breast cancer treatment: a review. JAMA. 2019;321:288–300. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
