Impact of fast-track surgery-oriented care pathways on perioperative rehabilitation indices in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer
- PMID: 38883357
- PMCID: PMC11170618
- DOI: 10.62347/ZMUX1738
Impact of fast-track surgery-oriented care pathways on perioperative rehabilitation indices in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer
Abstract
Objective: This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of Fast-Track Surgery (FTS)-oriented care pathways on perioperative rehabilitation indicators in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer.
Methods: The clinical data of 120 patients admitted to Sichuan Cancer Hospital & Institute who underwent radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer from September 2020 to October 2022 were collected and retrospectively analyzed. The patients were divided into a control group (n=60, receiving standard care) and an FTS group (n=60 patients receiving FTS-oriented care) according to different nursing methods. The perioperative rehabilitation indices were compared between the groups.
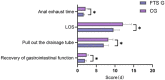
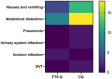
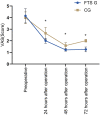
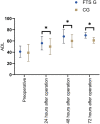
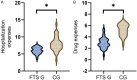
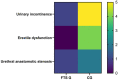
Results: The FTS group exhibited shorter hospitalization duration (P=0.001), postoperative anal exhaust time (P=0.012), drain removal time (P=0.007), gastrointestinal recovery time (P=0.008), and a lower total complication rate (P=0.016) compared to the control group. The scores of Visual Analog Scale (VAS) (P=0.001, P=0.003, P=0.015) and Activities of Daily Living (ADL) (P=0.011, P=0.005, P=0.007) at 24, 48, and 72 hours postoperatively were significantly lower in the FTS group than in the control group. Hospitalization cost (P=0.002) and medication expenses (P=0.016) were notably lower in the FTS group. During a 12-month follow-up, the FTS group showed a significantly lower complication rates (3.33%) compared to the control group (18.33%) (P=0.009).
Conclusion: The application of FTS-oriented nursing pathway in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer significantly enhances postoperative rehabilitation, reduces pain, lowers hospitalization and medication costs, and improves postoperative quality of life, which contributes positively to the nurse-patient relationship and patient outcome.
Keywords: Accelerated rehabilitation; fast-track surgery-oriented nursing pathway; pain management; perioperative rehabilitation indices; prostate cancer; quality of life; radical prostatectomy.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Impact of fast-track surgery on perioperative care in patients undergoing hepatobiliary surgery.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2024 Oct 27;16(10):3155-3162. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i10.3155. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2024. PMID: 39575282 Free PMC article.
-
Fast track surgery nursing models accelerate physical rehabilitation in perioperative patients undergoing hepatobiliary surgery.Am J Transl Res. 2025 Apr 15;17(4):2976-2983. doi: 10.62347/CQCF2993. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40385016 Free PMC article.
-
Fast-track surgery in single-hole thoracoscopic radical resection of lung cancer.J BUON. 2020 Jul-Aug;25(4):1745-1752. J BUON. 2020. PMID: 33099909
-
Enhanced recovery after surgery or fast-track surgery and the perioperative period of acute gastrointestinal perforation: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Surg. 2025 Apr 11;12:1529279. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1529279. eCollection 2025. Front Surg. 2025. PMID: 40292413 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of fast track surgery for patients with gastric cancer undergoing gastrectomy.Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2015 Jan;97(1):3-10. doi: 10.1308/rcsann.2015.97.1.3. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2015. PMID: 25519256 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cicero AFG, Allkanjari O, Busetto GM, Cai T, Larganà G, Magri V, Perletti G, Robustelli Della Cuna FS, Russo GI, Stamatiou K, Trinchieri A, Vitalone A. Nutraceutical treatment and prevention of benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2019;91:139–152. - PubMed
-
- Zhu Y, Freedland SJ, Ye D. Prostate cancer and prostatic diseases best of Asia, 2019: challenges and opportunities. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2020;23:197–198. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
