The effect of various interventions on the prevention of radiation dermatitis: a network meta-analysis
- PMID: 38883361
- PMCID: PMC11170609
- DOI: 10.62347/XLGT5405
The effect of various interventions on the prevention of radiation dermatitis: a network meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: High doses of radiation, while effective at destroying tumor tissues, also result in radiation dermatitis (RD) at irradiated sites, which is one of the most common complications in cancer radiotherapy. Currently, no standardized protocols for the prevention and treatment of RD have been established in clinical practices, and severe RD can compromise treatment efficacy and reduce patients' quality of life. This systematic review and network meta-analysis (NMA) aims to compare the effectiveness of various interventions in preventing RD in patients.
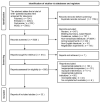
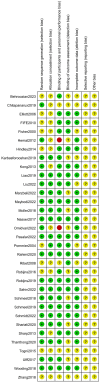
Methods: As of June 2023, four databases, including PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library, were searched, with a total of 19 interventions obtained for comparative analysis of their effectiveness in preventing RD. The Cochrane risk-of-bias tool was employed to screen literature, extract data, and appraise the quality of the studies by two researchers. Bayesian network meta-analysis (NMA) was conducted utilizing StataSE 15 and R 4.2.3.
Results: A total of 33 studies involving 4307 patients were included in this analysis. From the 33 studies, 19 interventions, encompassing Barrier Films and Dressings (BFD), Boron_Gel, Best supportive care, Corticosteroids_cream, Doxepin_cream, Eau Thermale Avèn_gel, Epidermal Growth Factor_cream, Hyaluronan_cream, Medicinal_Plants, Mineral_Oil, Olive oil and calcium hydroxide (OOCH), Photobiomodulation therapy, Recove_cream, Silicone_gel, Silver sulfadiazine (SSD), Timolol_Gel, Trolamine, VitD_Gel, and VitE_Gel, were retrieved and compared. The NMA results indicated that Hyaluronan_cream (SUCRA: 94.9%) was highly effective in preventing Grade 0/1 RD. Meanwhile, OOCH (SUCRA: 95.7%) demonstrated the most prominent effect in preventing ≥ Grade 2 RD.
Conclusion: The study reveals that Hyaluronan_cream and OOCH are two promising treatments for the prevention of RD in patients undergoing radiotherapy. Future research might focus on validating the efficacy of these two therapies with large sample sizes and on identifying an optimal intervention strategy.
Keywords: Radiation dermatitis; clinical efficacy; network meta-analysis; radiotherapy; topical interventions.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Comparison of the efficacy among different interventions for radiodermatitis: A Bayesian network meta‑analysis of randomized controlled trials.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 10;19(4):e0298209. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298209. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38598529 Free PMC article.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
The Effect of Sanyrene Liquid Dressing in Preventing Radiation Dermatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Adv Skin Wound Care. 2022 Nov 1;35(11):1-8. doi: 10.1097/01.ASW.0000889852.91765.ad. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2022. PMID: 36264754
-
Chinese herbal injections versus intrapleural cisplatin for lung cancer patients with malignant pleural effusion: A Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 20;12:942941. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.942941. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36203451 Free PMC article.
-
Combining various acupuncture therapies with multimodal analgesia to enhance postoperative pain management following total knee arthroplasty: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Neurol. 2024 Mar 18;15:1361037. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1361037. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38562427 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prevention and management of radiodermatitis in patients with brachytherapy for gynecologic neoplasms summary of the evidence.Front Oncol. 2025 Aug 8;15:1645101. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1645101. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40860836 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rzepecki A, Birnbaum M, Ohri N, Daily J, Fox J, Bodner W, Kabarriti R, Garg M, Mehta K, Kalnicki S, McLellan BN. Characterizing the effects of radiation dermatitis on quality of life: a prospective survey-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:161–163. - PubMed
-
- Guangmei D, Weishan H, Wenya L, Fasheng W, Jibing C. Evolution of radiation-induced dermatitis treatment. Clin Transl Oncol. 2024;3:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Wilson BN, Shah R, Menzer C, Aleisa A, Sun MD, Kwong BY, Kaffenberger BH, Seminario-Vidal L, Barker CA, Stubblefield MD, Romesser PB, Fabbrocini G, Alam M, Abdulla F, Dulmage B, Sibaud V, Anadkat M, Mazer JM, Parikh D, McLellan B, Cartier H, Pugliese S, Wolkerstorfer A, Laubach HJ, LeBoeuf N, Leventhal J, Wan DC, Choi J, Tran TN, Anderson RR, Markova A, Rossi A. Consensus on the clinical management of chronic radiation dermatitis and radiation fibrosis: a Delphi survey. Br J Dermatol. 2022;187:1054–1056. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
