Effects of TCM external scalding therapy on spleen-stomach deficiency cold stomachache and inflammatory indexes
- PMID: 38883362
- PMCID: PMC11170582
- DOI: 10.62347/MDQV6936
Effects of TCM external scalding therapy on spleen-stomach deficiency cold stomachache and inflammatory indexes
Abstract
Objective: To determine the efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) external scalding therapy on spleen-stomach deficiency cold stomachache.
Methods: The medical records of 98 patients with spleen-stomach deficiency cold stomachache treated in the Affiliated Hospital of Jiangnan University from January 2019 to January 2020 were collected and analyzed retrospectively. Among them, 52 patients treated with western medicine were assigned to the control group, while the other 46 patients treated additionally with TCM external scalding therapy were assigned to the observation group. The two groups were compared in terms of serum gastrin (GAS), inflammatory factors and visual analogue scale (VAS) score, adverse reaction rate and symptom remission time.
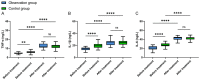
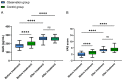
Results: After treatment, the observation group showed a significantly lower GAS level than the control group (P<0.05), along with significantly lower serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) than the control group (all P<0.05). The observation group demonstrated significantly lower VAS score than the control group (P<0.05). The observation group experienced notably shorter remission time of dull epigastric pain, epigastric distension, fatigue and belching and acid reflux than the control group (all P<0.05), and a significantly lower incidence of adverse reactions was found in the observation group than that in the control group (P<0.05). Multivariate analysis revealed that history of alcoholism and treatment method were independent risk factors affecting patient outcomes (all P<0.05).
Conclusion: TCM external scalding therapy has shown effectiveness in treating spleen-stomach deficiency cold stomachache. It alleviates stomachache symptoms and also reduces the occurrence of adverse reactions and inflammation, holding great potential for widespread adoption in clinical practice.
Keywords: External scalding therapy; multivariate analysis; spleen-stomach deficiency cold stomachache; traditional Chinese medicine.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulating spleen and stomach can improve bone and joint function of knee osteoarthritis patients complicated with osteoporosis.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Sep 15;15(9):5769-5777. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37854227 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical effects of a traditional Chinese medicine nursing programme to intervene in gastric pain of the spleen and stomach with Qi deficiency.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Jul 26;11(21):5056-5062. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i21.5056. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 37583847 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical research of acupuncture therapy combined with domperidone in treatment of diabetic gastroparesis of liver stagnation and spleen deficiency].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023 Jan 25;48(1):88-94. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20211215. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023. PMID: 36734504 Chinese.
-
Effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine on Serum Cytokines for the Dampness-heat Syndrome of Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Altern Ther Health Med. 2023 Jul;29(5):386-395. Altern Ther Health Med. 2023. PMID: 37171947
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine for the Common Cold: Evidence and Potential Mechanisms.Am J Chin Med. 2023;51(3):487-515. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X23500258. Epub 2023 Feb 18. Am J Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 36803206 Review.
References
-
- Lambert C, Mahevas T, Gobert D, Bravetti M, Radzik A, Poujol-Robert A, Ghrenassia E, Fain O. Epigastric pain. Rev Med Interne. 2022;43:260–261. - PubMed
-
- Huang CH, Lien WC, Wang HP. Man with epigastric pain. Ann Emerg Med. 2022;79:e107–e108. - PubMed
-
- Song J, Yang L, Su S, Piao MY, Li BL, Yu Y, Yu WY, Zhang M, Liang LX, Zuo GW, Tang ZM, Long YQ, Chen XL, Dai N, Mo JL, Wang RQ, Chen J, Hou XH. Agreement of gastroenterologists in traditional Chinese medical differential diagnosis of functional dyspepsia compared with traditional Chinese medical practitioners: a prospective, multicenter study. J Dig Dis. 2020;21:399–405. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
