FBXL18 is required for ovarian cancer cell proliferation and migration through activating AKT signaling
- PMID: 38883375
- PMCID: PMC11170572
- DOI: 10.62347/HHXX8166
FBXL18 is required for ovarian cancer cell proliferation and migration through activating AKT signaling
Abstract
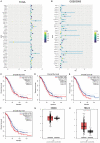
Background: F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 18 (FBXL18) is an F-box protein that functions as an E3-ubiquitin ligase, and it plays pivotal roles in multiple disease processes. However, its role and underlying mechanism in ovarian cancer (OC) are still unknown. We investigated the impact and mechanism of FBXL18 in OC cell growth and tumorigenesis.
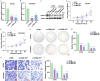
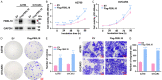
Methods: Silent interfering RNAs and overexpression plasmids were employed to knock down and overexpress FBXL18 in OC cells (A2780 and OVCAR3). CCK-8, colony formation, cell migration, and nude mouse xenograft assays were used to assess the effect of FBXL18 on OC cell proliferation and migration. Western blotting and co-immunoprecipitation followed by ubiquitination assays were performed to detect the mechanism of the FBXL18/AKT axis in OC.
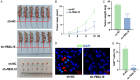
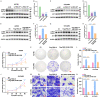
Results: FBXL18 knockdown inhibited OC cell proliferation and migration, whereas FBXL18 overexpression showed the opposite results. Phosphorylated-AKT (S473) protein expression was increased by FBXL18 overexpression and markedly decreased after phosphorylated-AKT inhibitor (MK-2206) treatment. Co-immunoprecipitation assays demonstrated that FBXL18 strongly interacted with AKT in OC cells. Ubiquitination assays revealed that FBXL18 promoted K63-linked AKT ubiquitination to activate AKT. MK-2206 treatment reversed the increase in proliferation and migration of OC cells induced by FBXL18 overexpression.
Conclusions: FBXL18 promoted OC cell proliferation and migration and facilitated OC tumorigenesis. Mechanically, FBXL18 interacted with AKT and promoted K63-linked ubiquitination of AKT to activate AKT in OC cells. Our study revealed that the FBXL18/AKT axis plays a crucial role in the OC process, indicating that FBXL18 may be a valuable target for OC diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: AKT; FBXL18; cell proliferation; migration; ovarian cancer.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
FBXL18 promotes endometrial carcinoma progression via destabilizing DUSP16 and thus activating JNK signaling pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 May 17;25(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03808-9. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 40382593 Free PMC article.
-
FBXL18 increases cell proliferation and reduces cell radiosensitivity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Strahlenther Onkol. 2025 Feb 19. doi: 10.1007/s00066-025-02373-4. Online ahead of print. Strahlenther Onkol. 2025. PMID: 39971770
-
The F-box protein FBXL18 promotes glioma progression by promoting K63-linked ubiquitination of Akt.FEBS Lett. 2017 Jan;591(1):145-154. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12521. Epub 2016 Dec 20. FEBS Lett. 2017. PMID: 27926990
-
Elevated FBXL18 promotes RPS15A ubiquitination and SMAD3 activation to drive HCC.Hepatol Commun. 2023 Jun 28;7(7):e00198. doi: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000198. eCollection 2023 Jul 1. Hepatol Commun. 2023. PMID: 37378633 Free PMC article.
-
OCT4 induces EMT and promotes ovarian cancer progression by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 10;12:876257. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.876257. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36033461 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
FBXL18 promotes endometrial carcinoma progression via destabilizing DUSP16 and thus activating JNK signaling pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 May 17;25(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03808-9. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 40382593 Free PMC article.
-
FBXL18 increases cell proliferation and reduces cell radiosensitivity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Strahlenther Onkol. 2025 Feb 19. doi: 10.1007/s00066-025-02373-4. Online ahead of print. Strahlenther Onkol. 2025. PMID: 39971770
References
-
- Nguyen KM, Busino L. The biology of F-box proteins: the SCF family of E3 ubiquitin ligases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1217:111–122. - PubMed
-
- Uddin S, Bhat AA, Krishnankutty R, Mir F, Kulinski M, Mohammad RM. Involvement of F-BOX proteins in progression and development of human malignancies. Semin Cancer Biol. 2016;36:18–32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
