Post-operative infections after cardiothoracic surgery and vascular procedures: a bibliometric and visual analysis of the 100 most-cited articles in the past 2 decades
- PMID: 38883404
- PMCID: PMC11177225
- DOI: 10.3205/dgkh000484
Post-operative infections after cardiothoracic surgery and vascular procedures: a bibliometric and visual analysis of the 100 most-cited articles in the past 2 decades
Abstract
Aim: To recognize and analyze the 100 most-cited articles on post-operative infections following cardiothoracic surgery and vascular procedures in the past 20 years.
Methods: Articles published on post-operative infections following cardiothoracic surgery and vascular procedures from inception 1986 till 2020 were reviewed and selected by two authors, based on their number of citations using the Scopus database. Their characteristics were recorded, i.e., title, authors, publication date, total no. of citations, citations per year (CPY), country of research, institutional affiliation, journal, research subject, and article type.
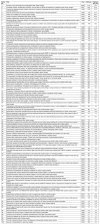
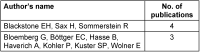
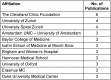
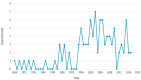
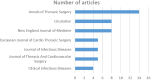
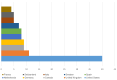
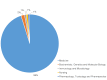
Results: The top 100 most influential articles were published between 1968 and 2017, with the peak in 2002. The mean number of total citations was 236.79 (range: 108-1,157). Areas with a medical focus were predominant in the studied research articles on the researched topic. The top-most journals in which these articles were published include Annals of Thoracic Surgery (14), followed by Circulation (8), and the New England Journal of Medicine (8). The number of publications affiliated with an institution were highest in the United States, with the Cleveland Clinic Foundation (6) having the most.
Conclusion: These findings highlight that there is a great potential to conduct research and publish the prevalence, causes, risk factors, pathogenesis and molecular biology of post-cardiac and -vascular surgery infections to prevent their adverse effects. The results can be taken into consideration for policy making to improve post-cardiac-surgery outcomes.
Zielsetzung: Erfassen und analysieren der 100 meist zitierten Artikel über postoperative Infektionen nach kardiothorakalen und vaskulären Eingriffen in den letzten Jahren.
Methode: Artikel über postoperative Infektionen nach kardiothorakalen Operationen und vaskulären Eingriffen, die von 1986 bis 2020 veröffentlicht wurden, wurden von zwei Autoren anhand der Anzahl der Zitate in der Scopus-Datenbank gesichtet, ausgewählt, und ihre Merkmale erfasst wie Titel, Autoren, Veröffentlichungsdatum, Gesamtzahl der Zitate, Zitate pro Jahr, Land der Forschung, institutionelle Zugehörigkeit, Zeitschrift, Forschungsthema und Art des Artikels.
Ergebnisse: Die 100 wichtigsten Artikel wurden zwischen 1968 und 2017 veröffentlicht, wobei der Höhepunkt im Jahr 2002 lag. Der Mittelwert der Gesamtzitationen betrug 236,79 (Spanne: 108–1.157). Bei den analysierten Artikeln überwiegen medizinisch ausgerichtete Bereiche. Zu den wichtigsten Zeitschriften, in denen die Artikel veröffentlicht wurden, gehören Annals of Thoracic Surgery (14), gefolgt von Circulation (8) und New England Journal of Medicine (8). Die Zahl der Veröffentlichungen, die mit einer Einrichtung verbunden sind, ist in den Vereinigten Staaten am höchsten mit der Cleveland Clinic Foundation (6) an der Spitze.
Schlussfolgerung: Die Ergebnisse zeigen, dass ein großes Potenzial für die Erforschung der Prävalenz, Ursachen, Risikofaktoren, Pathogenese und Molekularbiologie von postoperativen Wundinfektionen nach herz- und gefäßchirurgischen Eingriffen besteht, um deren nachteilige Auswirkungen zu verhindern.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis; cardiothoracic surgery; surgical site infections; vascular surgery; visual analysis.
Copyright © 2024 Ali et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Bibliometric Analysis of the Most Cited Articles in Neurocritical Care Research.Neurocrit Care. 2019 Oct;31(2):365-372. doi: 10.1007/s12028-019-00731-6. Neurocrit Care. 2019. PMID: 31087256 Review.
-
Assessing the impact of publications: A bibliometric analysis of the top-cited articles from The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2023 May;165(5):1901-1916. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2022.09.031. Epub 2022 Sep 24. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2023. PMID: 37032579
-
Minimally-invasive cardiac surgery: a bibliometric analysis of impact and force to identify key and facilitating advanced training.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2022 Sep 16;17(1):236. doi: 10.1186/s13019-022-01988-3. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2022. PMID: 36114506 Free PMC article.
-
The 100 most influential publications in paracetamol poisoning treatment: a bibliometric analysis of human studies.Springerplus. 2016 Sep 13;5(1):1534. doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-3240-z. eCollection 2016. Springerplus. 2016. PMID: 27652107 Free PMC article.
-
A Bibliometric Analysis of the Most Cited Journal Articles in Kidney Transplantation.Cureus. 2023 Apr 25;15(4):e38104. doi: 10.7759/cureus.38104. eCollection 2023 Apr. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37252599 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gelijns AC, Moskowitz AJ, Acker MA, Argenziano M, Geller NL, Puskas JD, Perrault LP, Smith PK, Kron IL, Michler RE, Miller MA, Gardner TJ, Ascheim DD, Ailawadi G, Lackner P, Goldsmith LA, Robichaud S, Miller RA, Rose EA, Ferguson TB, Jr, Horvath KA, Moquete EG, Parides MK, Bagiella E, O'Gara PT, Blackstone EH Cardiothoracic Surgical Trials Network (CTSN) Management practices and major infections after cardiac surgery. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 Jul 29;64(4):372–381. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.04.052. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

