Assessing Swallowing and Mastication Using the Swallowing Proficiency for Eating and Drinking Protocol Among Healthy Adults
- PMID: 38883485
- PMCID: PMC11169404
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-024-04575-1
Assessing Swallowing and Mastication Using the Swallowing Proficiency for Eating and Drinking Protocol Among Healthy Adults
Abstract
Background: Objective evaluation of swallowing using single bolus consistency are popular among Speech-Language Pathologists (SLPs) but has limited generalization to other bolus consistencies. The Swallowing Proficiency for Eating and Drinking (SPEAD) test assesses the oral and pharyngeal phases of swallowing using three different consistencies.
Objectives: The aim of this study was to establish normative data for the SPEAD test among healthy individuals aged 20-79 years.
Method and materials: One hundred and twelve healthy adults recruited from the community were divided into three age groups (20-39.11, 40-59.11, & 60-79.11 years). Participants swallowing 100 g of water and thickened Electral, and 6.67 g of Parle Monaco was video recorded for data analysis.
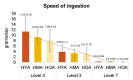
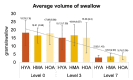
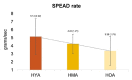
Results: Cronbachs Alpha test indicated good to excellent internal consistency and inter-class correlation test revealed a high level of inter-rater reliability for all SPEAD parameters. Older adults exhibited a higher number of bites, chews, and swallows, and required more time to swallow compared to younger and middle adults. Similarly, speed of ingestion and SPEAD rate were lowest in older adults. SPEAD indices also showed significant differences across the three consistencies at p < 0.01.
Conclusion: In summary, the SPEAD test was found to be feasible, reliable, and valid in healthy adults of India between 20 and 79 years of age. The age and sex based normative data established in this study will enable SLPs in assessing the presence and / or absence of swallowing difficulties in the oral and pharyngeal phases across different consistencies using one test.
Keywords: Healthy Adults; Solids; Swallowing Assessment; Thick Liquids; Thin Liquids.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing InterestsThe authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Test of mastication and swallowing solids in healthy individuals aged 6 to 20 years: A normative study in an Indian context.J Oral Rehabil. 2024 Sep;51(9):1839-1847. doi: 10.1111/joor.13741. Epub 2024 May 20. J Oral Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38767112
-
The Timed Swallowing Proficiency for Eating and Drinking (SPEAD) Test: Development and Initial Validation of an Instrument to Objectify (Impaired) Swallowing Capacity in Head and Neck Cancer Patients.Dysphagia. 2021 Dec;36(6):1072-1087. doi: 10.1007/s00455-020-10240-w. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Dysphagia. 2021. PMID: 33459852
-
The Test of Mastication and Swallowing Solids and the Timed Water Swallow Test: Reliability, associations, age and gender effects, and normative data.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023 Jan;58(1):67-81. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12768. Epub 2022 Aug 29. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023. PMID: 36036753 Free PMC article.
-
Surface electromyographic studies of swallowing in normal subjects: a review of 440 adults. Report 1. Quantitative data: timing measures.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004 Oct;131(4):548-55. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2004.03.013. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004. PMID: 15467634 Review.
-
Surface electromyographic studies of swallowing in normal subjects: a review of 440 adults. Report 2. Quantitative data: amplitude measures.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004 Nov;131(5):773-80. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2004.03.014. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004. PMID: 15523465 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-Term Outcomes of Dysphagia Rehabilitation With an Adjustable Resistance Training Device in Laryngectomized Individuals.Head Neck. 2025 Mar;47(3):801-812. doi: 10.1002/hed.27972. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Head Neck. 2025. PMID: 39440540 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Rangarathnam B, Desai RV. A preliminary survey of dysphagia practice patterns among speech-language pathologists in India. J Indian Speech Lang Hear Assoc. 2020;34:22. doi: 10.4103/JISHA.JISHA_20_19. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
