A Phase IIa Multicenter, Randomized, Vehicle-Controlled, Dose Escalating Study to Evaluate the Safety, Efficacy, and Pharmacokinetics of CBT-001 Ophthalmic Solution in Patients With Primary or Recurrent Pterygium
- PMID: 38883924
- PMCID: PMC11179250
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xops.2024.100502
A Phase IIa Multicenter, Randomized, Vehicle-Controlled, Dose Escalating Study to Evaluate the Safety, Efficacy, and Pharmacokinetics of CBT-001 Ophthalmic Solution in Patients With Primary or Recurrent Pterygium
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the safety and efficacy of CBT-001, a multitarget tyrosine kinase inhibitor eyedrop, for pterygia.
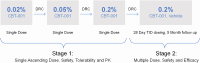
Design: Phase II clinical trial. Stage 1 was a single center, open-labeled, vehicle-controlled study. Stage 2 was a multicenter, randomized, double-masked, vehicle-controlled trial.
Participants: Patients with primary or recurrent pterygia.
Main outcome measures: The primary efficacy end point was lesion vascularity based on masked grading of photographs by an independent reading center. Other end points included dimensions of pterygia and safety.
Methods: In stage 1, 24 eyes of 24 patients received 1 drop of CBT-001 in a dose escalation fashion (0.02%, 0.05%, and 0.2%) to determine the maximally tolerated dose based on adverse events (AEs) and blood drug levels. In stage 2, subjects were randomly assigned to receive the maximally tolerated dose of CBT-001 or vehicle dosed 3 times a day for 4 weeks with a 20-week follow-up.
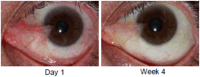
Results: In stage 1, the plasma maximum concentration values for all doses of CBT-001 were at or below the limit of detection (0.01 ng/ml). The most commonly reported AEs were mild foreign body sensation and irritation. CBT-001 0.2% was evaluated in stage 2. Baseline demographic characteristics were similar between patients receiving CBT-001 (n = 25) and vehicle (n = 23). After 4 weeks of dosing, the mean change from baseline in pterygium vascularity scores was -0.8 ± 0.7 (mean ± standard deviation) in subjects receiving CBT-001 0.2% and 0.0 ± 0.5 in subjects receiving vehicle (P < 0.001; 95% confidence interval: -1.12, -0.40). Pterygium vascularity scores remained significantly decreased, after the 4-week dosing period, at weeks 8 and 16, but not at week 24. The mean changes from baseline in the length of the pterygia were also significantly lower in subjects receiving CBT-001 compared with vehicle at weeks 2, 4, and 8 (P ≤ 0.014). The most commonly reported AEs were ocular, mild in severity, resolved after therapy, and did not result in discontinuation.
Conclusions: CBT-001 0.2% decreased pterygia vascularity and lesion length after 4 weeks of dosing with a prolonged effect after dosing. The drug was well tolerated with minimal detected systemic drug levels.
Financial disclosures: Proprietary or commercial disclosure may be found in the Footnotes and Disclosures at the end of this article.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Cornea; Pterygium; Tyrosine kinase inhibitor; Vascular endothelial growth factor.
© 2024 by the American Academy of Ophthalmology.
Figures



References
-
- Chui J., Coroneo M.T. In: Pterygium: Techniques and Technologies for Surgical Success. Hovanesian J.A., editor. SLACK Incorporated; Thorofare, NJ: 2012. Pterygium pathogenesis, actinic damage, and recurrence; pp. 1–26.
-
- Abraham A.P., Brooks G., Dadas C., et al. Prevalence of pterygium in the United States: a claims-based analysis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023;64:1173.
-
- Fernandes A.G., Salomao S.R., Ferraz N.N., et al. Pterygium in adults from the Brazilian Amazon Region: prevalence, visual status and refractive errors. Br J Ophthalmol. 2020;104:757–763. - PubMed
-
- Buratto L., Phillips R.L., Carito G. SLACK Incorporated; Thorofare, NJ: 2000. Pterygium Surgery.
-
- Di Girolamo N., Chui J., Coroneo M.T., Wakefield D. Pathogenesis of pterygia: role of cytokines, growth factors, and matrix metalloproteinases. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2004;23:195–228. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

