MR histology reveals tissue features beneath heterogeneous MRI signal in genetically engineered mouse models of sarcoma
- PMID: 38884083
- PMCID: PMC11176416
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1287479
MR histology reveals tissue features beneath heterogeneous MRI signal in genetically engineered mouse models of sarcoma
Abstract
Purpose: To identify significant relationships between quantitative cytometric tissue features and quantitative MR (qMRI) intratumorally in preclinical undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcomas (UPS).
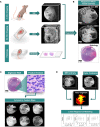
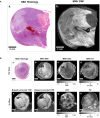
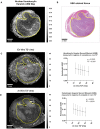
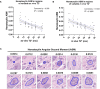
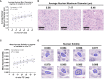
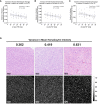
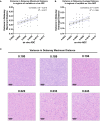
Materials and methods: In a prospective study of genetically engineered mouse models of UPS, we registered imaging libraries consisting of matched multi-contrast in vivo MRI, three-dimensional (3D) multi-contrast high-resolution ex vivo MR histology (MRH), and two-dimensional (2D) tissue slides. From digitized histology we generated quantitative cytometric feature maps from whole-slide automated nuclear segmentation. We automatically segmented intratumoral regions of distinct qMRI values and measured corresponding cytometric features. Linear regression analysis was performed to compare intratumoral qMRI and tissue cytometric features, and results were corrected for multiple comparisons. Linear correlations between qMRI and cytometric features with p values of <0.05 after correction for multiple comparisons were considered significant.
Results: Three features correlated with ex vivo apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), and no features correlated with in vivo ADC. Six features demonstrated significant linear relationships with ex vivo T2*, and fifteen features correlated significantly with in vivo T2*. In both cases, nuclear Haralick texture features were the most prevalent type of feature correlated with T2*. A small group of nuclear topology features also correlated with one or both T2* contrasts, and positive trends were seen between T2* and nuclear size metrics.
Conclusion: Registered multi-parametric imaging datasets can identify quantitative tissue features which contribute to UPS MR signal. T2* may provide quantitative information about nuclear morphology and pleomorphism, adding histological insights to radiological interpretation of UPS.
Keywords: MRI; feature mapping; histology; image registration; multi-modal; preclinical; sarcoma.
Copyright © 2024 Blocker, Mowery, Everitt, Cook, Cofer, Qi, Bassil, Xu, Kirsch, Badea and Johnson.
Conflict of interest statement
DK is a co-founder of XRAD Therapeutics, which is commercializing radiosensitizers. DK is on the scientific advisory board for Lumicell, which is commercializing intraoperative imaging technology. DK has received research support from Merck, XRAD Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Varian. However, this funding did not support this work. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Magnetic resonance perfusion for differentiating low-grade from high-grade gliomas at first presentation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 22;1(1):CD011551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29357120 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying multi-institutional ADC measurement variability of 1.5 T MR-Linacs: A phantom and in vivo study.Med Phys. 2025 Jun;52(6):4120-4133. doi: 10.1002/mp.17739. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40079445 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the associations between features from multi-parametric MR images in Glioblastoma using radiomics.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01788-w. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40596920 Free PMC article.
-
MRI-derived Articular Cartilage Strains Predict Patient-Reported Outcomes Six Months Post Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 29:2024.04.27.24306484. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.27.24306484. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21426. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05306-4. PMID: 38746083 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Fletcher CD, Dal Cin P, de Wever I, Mandahl N, Mertens F, Mitelman F, et al. . Correlation between clinicopathological features and karyotype in spindle cell sarcomas. A report of 130 cases from the CHAMP study group. Am J Pathol. (1999) 154:1841–7. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65441-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

