Angiotensin Receptor Blockers for Hypertension and Risk of Epilepsy
- PMID: 38884986
- PMCID: PMC11184499
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2024.1714
Angiotensin Receptor Blockers for Hypertension and Risk of Epilepsy
Abstract
Importance: Animal and human studies have suggested that the use of angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) may be associated with a lower risk of incident epilepsy compared with other antihypertensive medications. However, observational data from the US are lacking.
Objective: To evaluate the association between ARB use and epilepsy incidence in subgroups of US patients with hypertension.
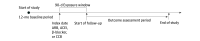
Design, setting, and participants: This retrospective cohort study used data from a national health administrative database from January 2010 to December 2017 with propensity score (PS) matching. The eligible cohort included privately insured individuals aged 18 years or older with diagnosis of primary hypertension and dispensed at least 1 ARB, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI), β-blocker, or calcium channel blocker (CCB) from 2010 to 2017. Patients with a diagnosis of epilepsy at or before the index date or dispensed an antiseizure medication 12 months before or 90 days after initiating the study medications were excluded. The data analysis for this project was conducted from April 2022 to April 2024.
Exposures: Propensity scores were generated based on baseline covariates and used to match patients who received ARBs with those who received either ACEIs, β-blockers, CCBs, or a combination of these antihypertensive medications.
Main outcomes and measures: Cox regression analyses were used to evaluate epilepsy incidence during follow-up comparing the ARB cohort with other antihypertensive classes. Subgroup and sensitivity analyses were conducted to examine the association between ARB use and epilepsy incidence in various subgroups.
Results: Of 2 261 964 patients (mean [SD] age, 61.7 [13.9] years; 1 120 630 [49.5%] female) included, 309 978 received ARBs, 807 510 received ACEIs, 695 887 received β-blockers, and 448 589 received CCBs. Demographic and clinical characteristics differed across the 4 comparison groups prior to PS matching. Compared with ARB users, patients receiving ACEIs were predominantly male and had diabetes, CCB users were generally older (eg, >65 years), and β-blocker users had more comorbidities and concurrent medications. The 1:1 PS-matched subgroups included 619 858 patients for ARB vs ACEI, 619 828 patients for ARB vs β-blocker, and 601 002 patients for ARB vs CCB. Baseline characteristics were equally distributed between comparison groups after matching with propensity scores. Use of ARBs was associated with a decreased incidence of epilepsy compared with ACEIs (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.75; 95% CI, 0.58-0.96), β-blockers (aHR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.54-0.90), and a combination of other antihypertensive classes (aHR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.56-0.95). Subgroup analyses revealed a significant association between ARB use (primarily losartan) and epilepsy incidence in patients with no preexisting history of stroke or cardiovascular disease.
Conclusions and relevance: This cohort study found that ARBs, mainly losartan, were associated with a lower incidence of epilepsy compared with other antihypertensive agents in hypertensive patients with no preexisting stroke or cardiovascular disease. Further studies, such as randomized clinical trials, are warranted to confirm the comparative antiepileptogenic properties of antihypertensive medications.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association Between Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Therapy and Incidence of Epilepsy in Patients With Hypertension.JAMA Neurol. 2022 Dec 1;79(12):1296-1302. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.3413. JAMA Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36251288 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium Channel Blocker Versus Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitor in Risk of Kidney Cancer Among Patients With Hypertension: A Propensity Score-Matched Cohort Study.Cancer Med. 2024 Nov;13(22):e70429. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70429. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39548764 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Long-term Use of Antihypertensive Medications With Late Outcomes Among Patients With Aortic Dissection.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Mar 1;4(3):e210469. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0469. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 33656527 Free PMC article.
-
Role of antihypertensive therapy with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers in combination with calcium channel blockers for stroke prevention.J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2010 Sep-Oct;50(5):e116-25. doi: 10.1331/JAPhA.2010.09234. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2010. PMID: 20833609 Review.
-
Association Between Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors and Clinical Outcomes in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Mar 1;4(3):e213594. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.3594. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 33787911 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Risk Factors Associated With Late-Onset Epilepsy in Dementia and Mild Cognitive Impairment.JAMA Neurol. 2025 Jun 1;82(6):605-613. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2025.0552. JAMA Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40227723
-
Prognostic models for seizures and epilepsy after stroke, tumors and traumatic brain injury.Clin Neurophysiol Pract. 2025 Mar 4;10:116-128. doi: 10.1016/j.cnp.2025.02.008. eCollection 2025. Clin Neurophysiol Pract. 2025. PMID: 40160930 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gu Q, Burt VL, Dillon CF, Yoon S. Trends in antihypertensive medication use and blood pressure control among United States adults with hypertension: the National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey, 2001 to 2010. Circulation. 2012;126(17):2105-2114. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.096156 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hong S, JianCheng H, JiaWen W, et al. . Losartan inhibits development of spontaneous recurrent seizures by preventing astrocyte activation and attenuating blood-brain barrier permeability following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Brain Res Bull. 2019;149:251-259. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.05.002 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

