Simulation-Based Optimization of Sampling Schedules for Model-Informed Precision Dosing of Once-Daily and 4-Times-Daily Busulfan in Pediatric Patients
- PMID: 38885146
- PMCID: PMC11554249
- DOI: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000001217
Simulation-Based Optimization of Sampling Schedules for Model-Informed Precision Dosing of Once-Daily and 4-Times-Daily Busulfan in Pediatric Patients
Abstract
Background: Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is crucial in optimizing the outcomes of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation by guiding busulfan (Bu) dosing. Limited sampling strategies show promise for efficiently adjusting drug doses. However, comprehensive assessments and optimization of sampling schedules for Bu TDM in pediatric patients are limited. We aimed to establish optimal sampling designs for model-informed precision dosing (MIPD) of once-daily (q24h) and 4-times-daily (q6h) Bu administration in pediatric patients.
Methods: Simulated data sets were used to evaluate the population pharmacokinetic model-based Bayesian estimation of the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) for different limited sampling strategy designs. The evaluation was based on the mean prediction error for accuracy and root mean square error for precision. These findings were validated using patient-observed data. In addition, the MIPD protocol was implemented in the Tucuxi software, and its performance was assessed.
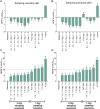
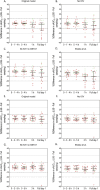
Results: Our Bayesian estimation approach allowed for flexible sampling times while maintaining mean prediction error within ±5% and root mean square error below 10%. Accurate and precise AUC 0-24h and cumulative AUC estimations were obtained using 2-sample and single-sample schedules for q6h and q24h dosing, respectively. TDM on 2 separate days was necessary to accurately estimate cumulative exposure, especially in patients receiving q6h Bu. Validation with observed patient data confirmed the precision of the proposed limited sampling scenarios. Implementing the MIPD protocol in Tucuxi software yielded reliable AUC estimations.
Conclusions: Our study successfully established precise limited sampling protocols for MIPD of Bu in pediatric patients. Our findings underscore the importance of TDM on at least 2 occasions to accurately achieve desired Bu exposures. The developed MIPD protocol and its implementation in Tucuxi software provide a valuable tool for routine TDM in pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
Keywords: busulfan; hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; limited sampling strategy; model-informed precision dosing; pediatric; therapeutic drug monitoring.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Model-Informed Precision Dosing of Busulfan for Children and Adults Undergoing Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Critical Evaluation of Current PK Models and Dose Recommendations.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2025 Sep;118(3):723-734. doi: 10.1002/cpt.3748. Epub 2025 Jun 22. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40545743 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Simulation with Pharmacogenetic Insights Support the Relevance of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring for Myeloablative Busulfan Dosing in Adult HSCT.Transplant Cell Ther. 2024 Mar;30(3):332.e1-332.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2023.12.003. Epub 2023 Dec 9. Transplant Cell Ther. 2024. PMID: 38081414
-
Model-Informed Precision Dosing of Intravenous Busulfan in Thai Pediatrics Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation.Ther Drug Monit. 2024 Dec 1;46(6):778-785. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000001225. Epub 2024 May 14. Ther Drug Monit. 2024. PMID: 38758634
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quality improvement strategies for diabetes care: Effects on outcomes for adults living with diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 May 31;5(5):CD014513. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014513. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37254718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klyuchnikov E, Langebrake C, Badbaran A, et al. Individualized busulfan dosing improves outcomes compared to fixed-dose administration in pre-transplant minimal residual disease-positive acute myeloid leukemia patients with intermediate-risk undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation in CR. Eur J Haematol. 2023;110:188–197. - PubMed
-
- Gurlek Gokcebay D, Arman Bilir O, Şahin S, et al. . Role of therapeutic drug monitoring of intravenous Busulfan for prevention of sinusoidal obstructive syndrome in children. Pediatr Transplant. 2022;26:e14266. - PubMed
-
- Hill BT, Rybicki LA, Urban TA, et al. Therapeutic dose monitoring of busulfan is associated with reduced risk of relapse in non-Hodgkin Lymphoma patients undergoing autologous stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020;26:262–271. - PubMed
-
- Faraci M, Tinelli C, Lanino E, et al. Monitoring of busulphan concentrations in children undergone hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: unicentric experience over 10 years. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2018;43:173–181. - PubMed
-
- Salman B, Al-Za’abi M, Al-Huneini M, et al. Therapeutic drug monitoring-guided dosing of busulfan differs from weight-based dosing in hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2017;10:70–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

